Circa 2016
MIT scientists have developed a 5-atom quantum computer, one that is able to render traditional encryption obsolete.
Circa 2016
MIT scientists have developed a 5-atom quantum computer, one that is able to render traditional encryption obsolete.
It is in this second phase when Darwinian evolutionary rivers will merge with the rivers of intelligent designers, represented by scientists, programmers and engineers, who will fuse organic natural biology, synthetic biology, and digital technology into a unified whole that future generations will deem their anatomy. The merger will serve to afford greater intelligence and, longer, healthier lives. In exchange, we will relinquish actual autonomy for apparent autonomy, where what was once considered “free will” will be supplanted by the deterministic logic of machinery somewhere in the mainstream of our unconscious.
Although in-the-body technology will have an explosive effect on commerce, entertainment, and employment, in the near term the concentration will be on medical devices, such as the innocuous pacemaker (essentially a working silicon-based computer, with sensors, memories, and a stimulation device with telecommunications to the outer world). In a second epoch, these devices will be gradually down-sized by advances in synthetic DNA, molecular- and nano-sized processors, each deployed alongside and within cells and organs as permanent non-organic, internal adjuncts to our anatomy for use as: nano-prosthetics, nano-stimulators/suppressors, artificial organ processors, metabolic and cognitive enhancers, and permanent diagnostic tools to ensure our physical and psychological well-being as we head toward a practically interminable lifetime.[6]
Will a wide-spread practice of installing technology into the body fundamentally change human essence? Our sense of self-sufficiency, authenticity, or individual identity? Will it change that numerical identity, the one “I” as some static aspect of ourselves (as self-consciousness as idealized by Locke)? Or will it change our narrative identity, our unseen internal human form, to eventually redefine what it means to be human?[7].

Now, five years later, their gamble appears to have paid off. Not only did New Horizons achieve a next-to flawless flyby of Arrokoth, the most distant object ever visited, but buried in its gigabytes of data—which have been trickling back to Earth ever since the New Year’s Day 2019 rendezvous—lies empirical evidence that strikes against a classic theory of how planets form. The New Horizons team published their latest analysis of the ancient body and how it came to be in a trio of papers appearing in Science last week.
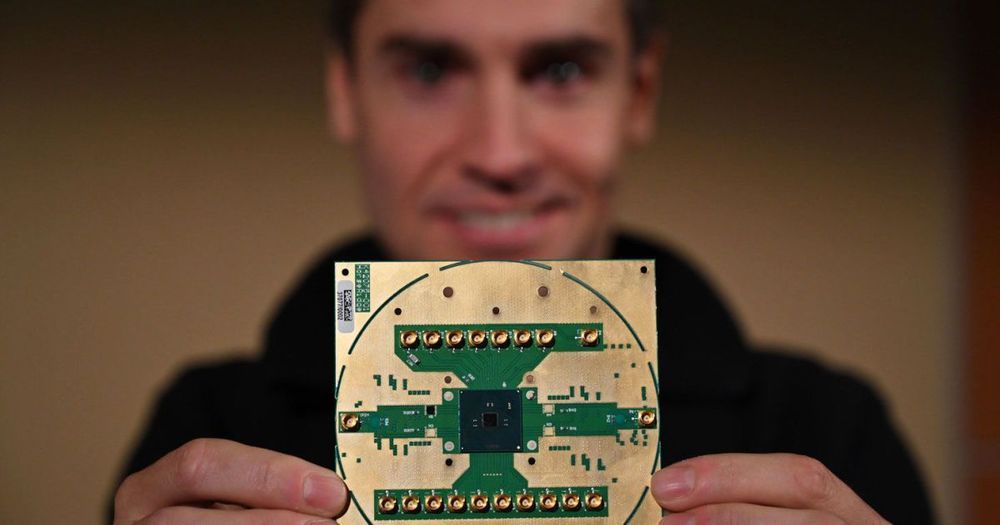
Labs around the world are racing to develop new computing and sensing devices that operate on the principles of quantum mechanics and could offer dramatic advantages over their classical counterparts. But these technologies still face several challenges, and one of the most significant is how to deal with “noise”—random fluctuations that can eradicate the data stored in such devices.
A new approach developed by researchers at MIT could provide a significant step forward in quantum error correction. The method involves fine-tuning the system to address the kinds of noise that are the most likely, rather than casting a broad net to try to catch all possible sources of disturbance.
The analysis is described in the journal Physical Review Letters, in a paper by MIT graduate student David Layden, postdoc Mo Chen, and professor of nuclear science and engineering Paola Cappellaro.


After being blind for 16 years, scientists have plugged a bionic eye directly into Bernardeta Gomez’s brain, allowing her to see again without using her biological eyes after she had a computer port surgically embedded into her skull.
The vision system is being honed by neuriengineer Eduardo Fernandez in his lab at the University of Miguel Hernandez, and it is comprised of a few different parts according to the publication in MIT Technology Review.
There is a pair of glasses that are fitted with a camera that connects to a computer which translates the live video feed into electronic signals that are then sent via a cable to the port which has been surgically embedded into the back of Gomez’s skull and connects to an implant in the visual cortex of her brain.

Coronvirus fears are being raised in earnings calls throughout different sectors as Wall Street looks for any effects from the virus spreading within and outside of China, which should lead to a lot of talk on what could be the busiest single day of the earnings season.
Nearly 10% of the S&P 500 index SPX, +0.18%, 46 components, are scheduled to report on Wednesday, along with four members of the blue-chip Dow Jones Industrial Average DJIA, −0.09% — Boeing Co. BA, −0.68%, Dow Inc. DOW, +0.68%, McDonald’s Corp. MCD, −0.15% and Microsoft Corp. MSFT, +0.89%.
The company on that list most linked to coronavirus fears is McDonald’s, which has had to temporarily shut down some of its stores in China due to fears about the outbreak. During the SARS crisis in the early 2000s, there was a “pronounced but relatively short-lived” impact on restaurant sales in the Greater China region, according to Bernstein analyst Sara Senatore. China accounts for only 2% of McDonald’s earnings and the company has only closed about 1% of its China stores so far, so expect executives to play down any effects when they report before the bell Wednesday.
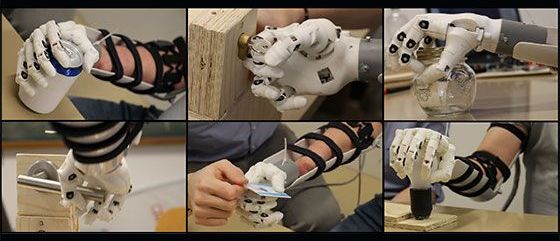
Prosthetic hands restore only some of the function lost through amputation. But combining electrical signals from forearm muscles with other sources of information, such as eye tracking, promises better prostheses. A study funded by the SNSF gives specialists access to valuable new data.
Page Content
The hand is a precious limb. Its 34 muscles and 20 joints enable movements of great precision and complexity which are essential for interacting with the environment and with others on a daily basis. Hand amputation thus has severe physical and psychological repercussions on a person’s life. Myoelectric prosthetic hands, which work by recording electrical muscle signals on the skin, allow amputees to regain some lost function. But dexterity is often limited and the variability of the electrical signals from the forearm alone makes the prosthetics sometimes unreliable. Henning Müller, professor of business informatics, is investigating how combining data from myoelectric signals with other sources of information could lead to better prosthetics. Müller has now made available to the scientific community a dataset that includes eye tracking and computer vision as well as other information (electromyography and acceleration sensor data).
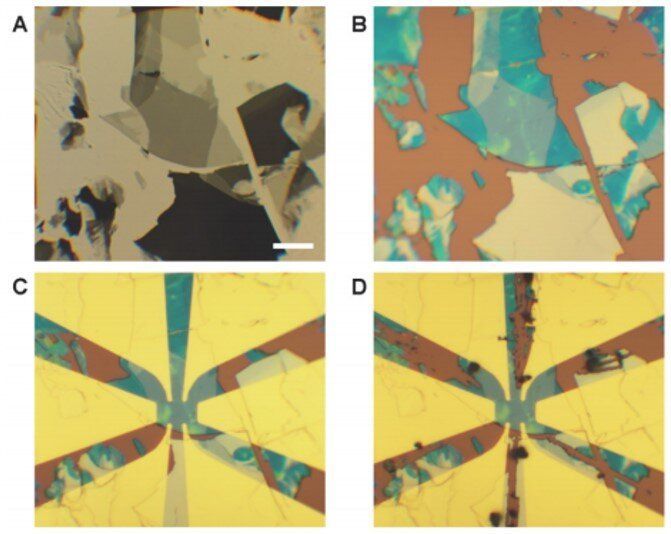
Nontrivial band topology can combine with magnetic order in a magnetic topological insulator to produce exotic states of matter such as quantum anomalous Hall (QAH) insulators and axion insulators. An aim of condensed matter physics is to find new materials with useful properties and apply quantum mechanics to study them. The field has allowed physicists to better understand the uses of magnets for hard disk data storage, computer displays and other technologies. The recent discovery of topological insulators have attracted broad interest and researchers predict that the interplay between ferromagnetism and the topological insulator state can realize a range of exotic quantum magnetic phenomena of interest in fundamental physics and device applications.
In a new report, Yujun Deng and a research team at the departments of physics and quantum matter physics in China, probed quantum transport in a thin flake MnBi2Te4 topological insulator, with intrinsic magnetic order. The ferromagnetic layers coupled anti-parallelly to each other in the atomically thin MnBi2Te4 layered van der Waals crystal. However, the sample became ferromagnetic when it contained an odd number of septuple layers. The research team observed the zero-field QAH effect in a five-septuple-layer specimen at 1.4 Kelvin. The results established MnBi2Te4 as an ideal platform to explore exotic topological phenomena with spontaneously broken time-reversal symmetry. The work is now published on Science.
Topological materials distinctly contain topologically protected quantum states that are robust against local distresses. For instance, in a topological insulator (TI) such as bismuth telluride (Bi2Te3), the bulk band topology can guarantee the existence of two-dimensional (2-D) surface states with gapless Dirac dispersion. By introducing magnetism into the initially time-reversal invariant topological insulators (TIs), scientists can induce profound changes in their electronic structure. For example, to experimentally observe the QAH effect in chromium-doped (Bi, Sb)2Te3, physicists had to precisely control the ratio of multiple elements in a non-stoichiometric material. Fine-tuning the material required reconciling conflicting demands and therefore, researchers had to precisely quantize the anomalous Hall effect only at temperatures up to T = 2 K, far below the Curie temperature and exchange gap in the material.