Circa 2011 essentially a magnet could be a battery and cpu and a gpu with magnonics.
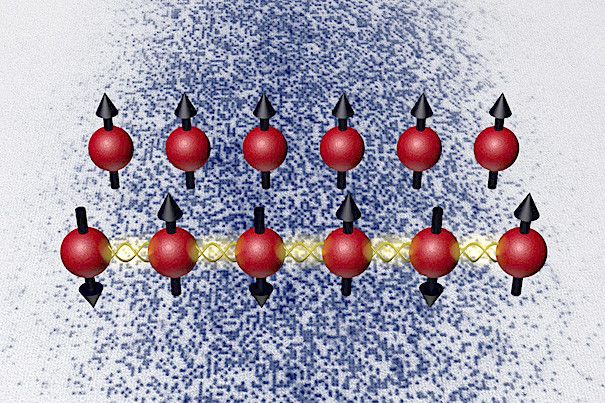
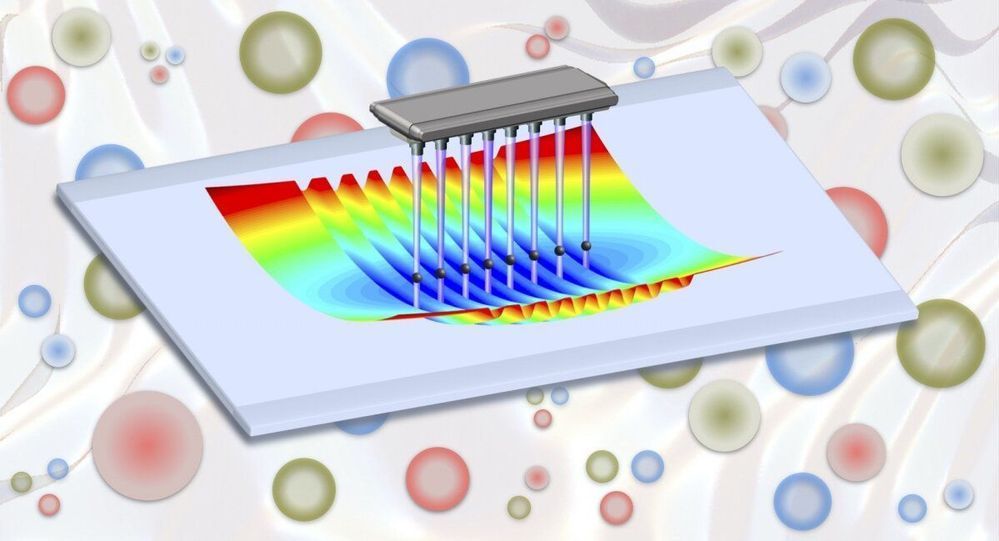
Harvard physicists have expanded the possibilities for quantum engineering of novel materials such as high-temperature superconductors by coaxing ultracold atoms trapped in an optical lattice — a light crystal — to self-organize into a magnet, using only the minute disturbances resulting from quantum mechanics. The research, published in the journal Nature, is the first demonstration of such a “quantum magnet” in an optical lattice.
As modern technology depends more and more on materials with exotic quantum mechanical properties, researchers are coming up against a natural barrier.
“The problem is that what makes these materials useful often makes them extremely difficult to design,” said senior author Markus Greiner, an associate professor in Harvard’s Department of Physics. “They can become entangled, existing in multiple configurations at the same time. This hallmark of quantum mechanics is difficult for normal computers to represent, so we had to take another approach.”