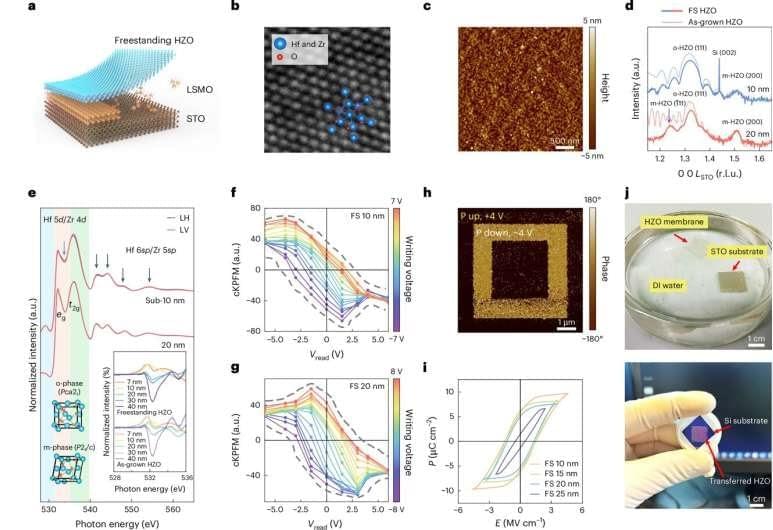
CERN scientists have analyzed a particle of antimatter isolated in an undecided quantum state known as a superposition for the first time.
While the quantum behavior of ordinary matter has been studied extensively and even used as the basis of quantum computers in the form of qubits, the breakthrough goes far beyond technological applications, potentially helping physicists understand why we even exist today.
The team suspended an antiproton – the antimatter counterpart of the proton – in a system of electromagnetic traps, and suppressed environmental interference that would mess with the particle’s delicate quantum state.