IBM and RIKEN demonstrate how hybrid quantum computing is solving complex molecular chemistry problems, marking a step toward real-world quantum advantage.


Bioelectronics have transformed our capacity to monitor and treat diseases; however, a lack of micrometer-scale, energy efficient communication options limit these devices from forming integrated networks that enable full-body, sensor driven, physiological control. Inspired by our nervous system’s ability to transmit information via ionic conduction, we engineered a Smart Wireless Artificial Nervous System (SWANS) that utilizes the body’s own tissue to transmit signals between wearables and implantables. When SWANS emits signals, it generates voltage gradients throughout the body that selectively turn on implanted transistor switches when exceeding their gate threshold voltages. SWANS’ implantable communication components maintain syringe-injectable footprints and 15x greater power efficiencies than Bluetooth and Near Field Communication. In vivo studies in rats demonstrate SWANS’ ability to wirelessly regulate dual hind leg motor control by connecting electronic-skin sensors to implantable neural interfaces via ionic signaling as well as coordinate bioelectronics throughout the epidermal, subcutaneous, intraperitoneal, and gastrointestinal spaces.
Ramy ghanim, yoon jae lee, garan byun, joy jackson, julia Z ding, elaine feller, eugene kim, dilay aygun, anika kaushik, alaz cig, jihoon park, sean healy, camille E cunin, aristide gumyusenge, woon hong yeo, alex abramson.
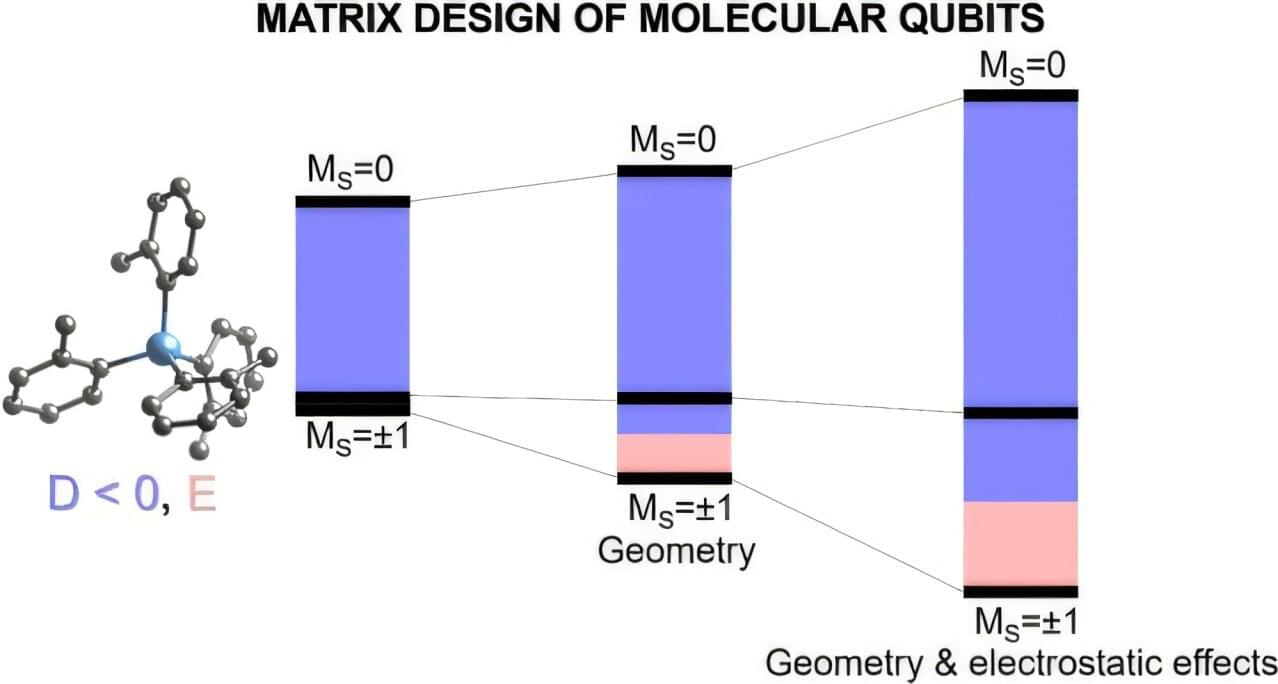
A qubit is the delicate, information-processing heart of a quantum device. In the coming decades, advances in quantum information are expected to give us computers with new, powerful capabilities and detectors that can pick up atomic-scale signals in medicine, navigation and more. The realization of such technologies depends on having reliable, long-lasting qubits.
Now, researchers have taken an important step in understanding the rules necessary for the design of useful, efficient qubits.
Using advanced computer modeling, the researchers came up with a way to accurately predict and fine-tune key magnetic properties of a type of device called a molecular qubit. They also figured out which factors in the material that the qubit sits in affect this tuning the most and calculated how long the qubits can live.

We’re often told it is “unscientific” or “meaningless” to ask what happened before the Big Bang. But a new paper by FQxI cosmologist Eugene Lim, of King’s College London, UK, and astrophysicists Katy Clough, of Queen Mary University of London, UK, and Josu Aurrekoetxea, at Oxford University, UK, published in Living Reviews in Relativity, proposes a way forward: using complex computer simulations to numerically (rather than exactly) solve Einstein’s equations for gravity in extreme situations.
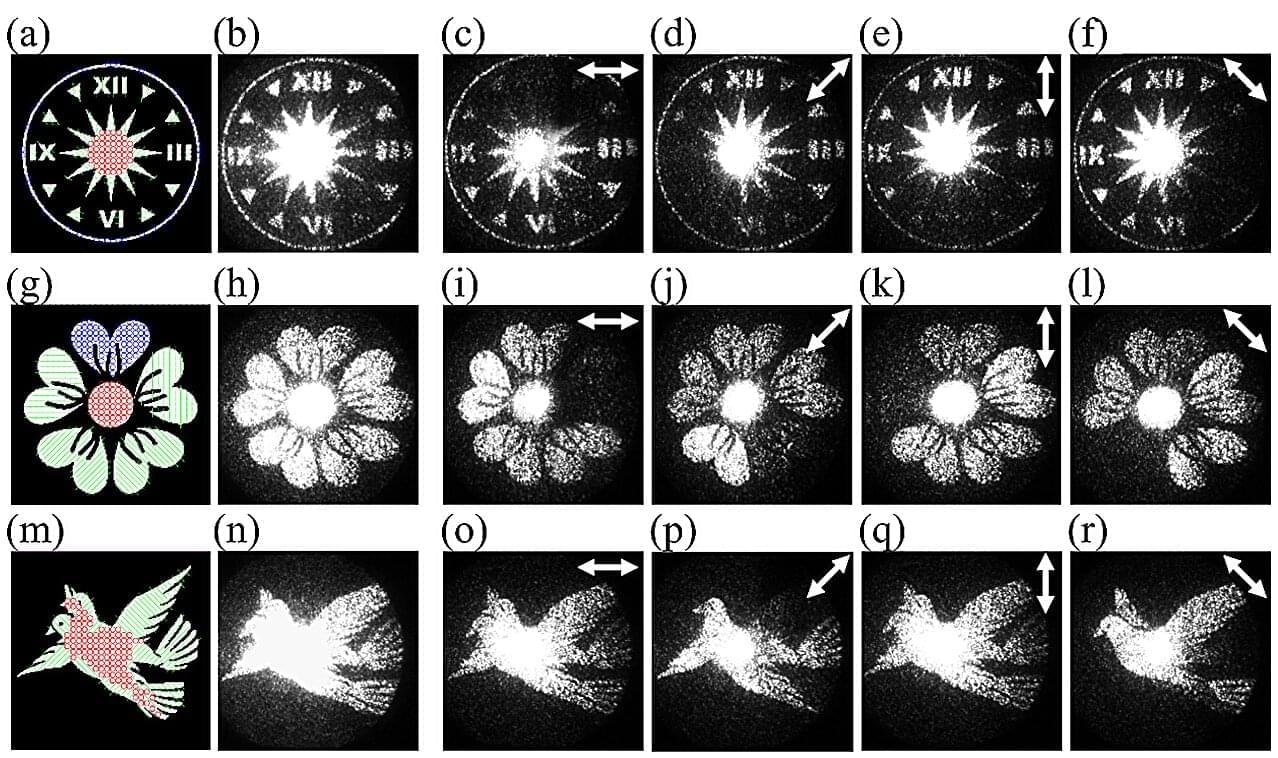
Holography—the science of recording and reconstructing light fields—has long been central to imaging, data storage, and encryption. Traditional holographic systems, however, rely on bulky optical setups and interference experiments, making them impractical for compact or integrated devices. Computational methods such as the Gerchberg–Saxton (GS) algorithm have simplified hologram design by eliminating the need for physical interference patterns, but these approaches typically produce scalar holograms with uniform polarization, limiting the amount of information that can be encoded.
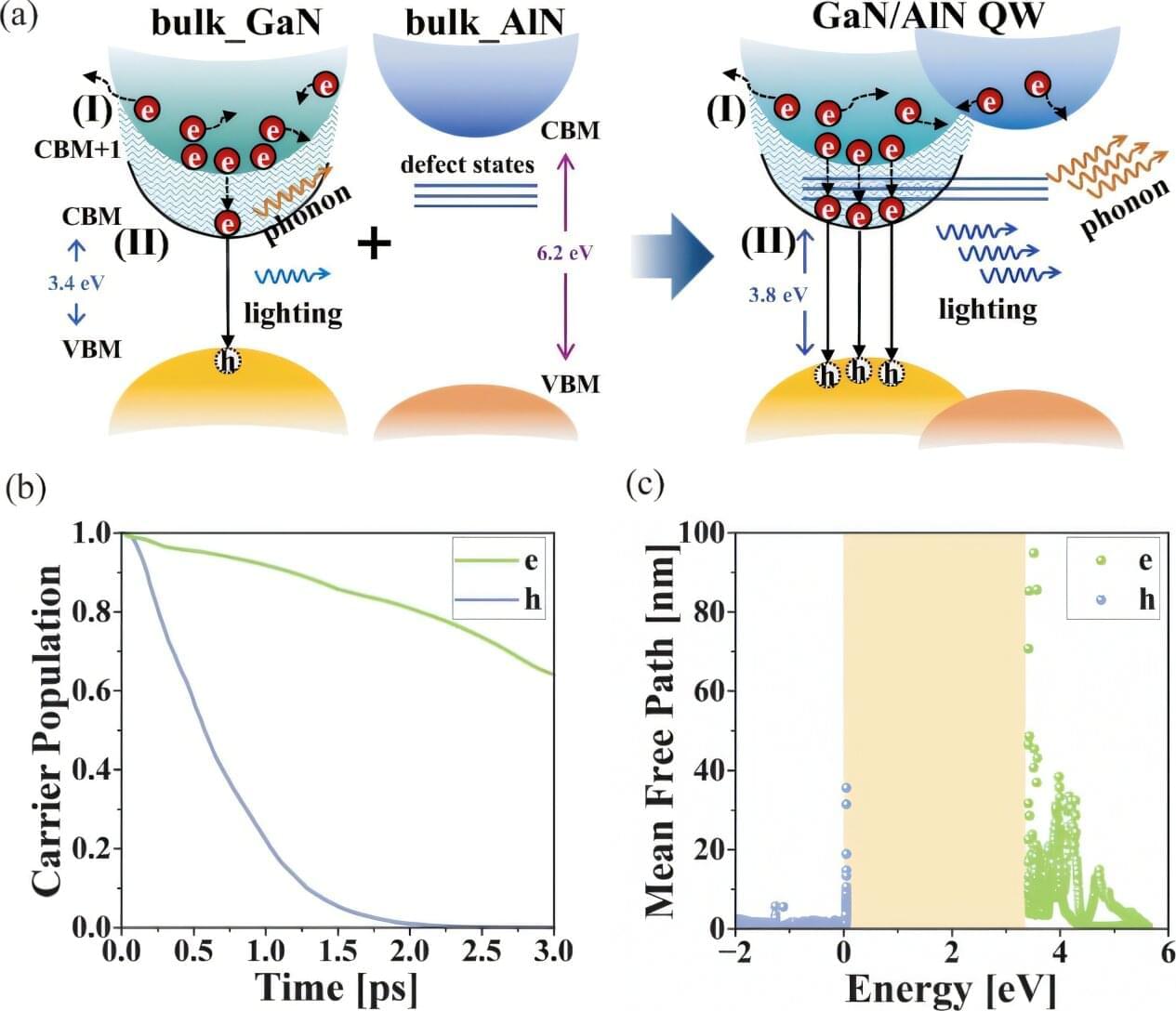
A study conducted by researchers from the Changchun Institute of Optics, Fine Mechanics and Physics (CIOMP) of the Chinese Academy of Sciences has demonstrated how nitrogen vacancies (VN) resolve asymmetric carrier injection in GaN-based light-emitting diodes (LEDs), providing a practical way to improve device efficiency.

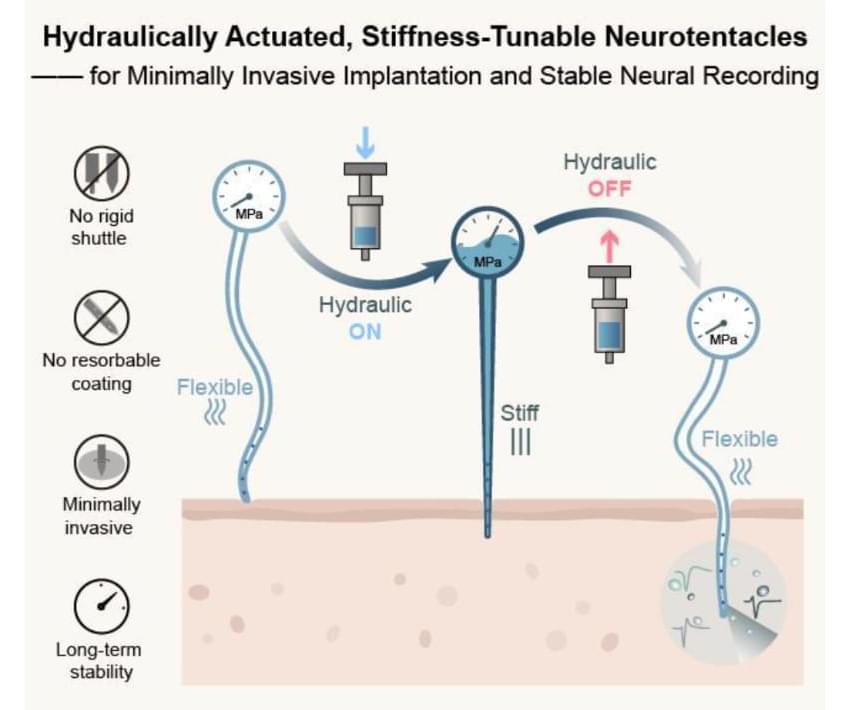
Chinese researchers have made significant progress in developing flexible invasive brain-computer interface implants, creating a stiffness-tunable “Neurotentacle” probe that can reduce implantation damage by 74 percent, Science and Technology Daily reported Tuesday.
The “Neurotentacle” probe developed by researchers at the Institute of Semiconductors, Chinese Academy of Sciences (CAS), contains a tiny hydraulic system. During the implantation, the hydraulically actuated “Neurotentacle” probe stiffens like an inflated balloon to precisely penetrate brain tissue. Once it is in place, it softens afterward to minimize damage and returns to a flexible state to adapt to the brain’s microenvironment, said the report.
The findings were published online in the international journal Advanced Science on July 21.
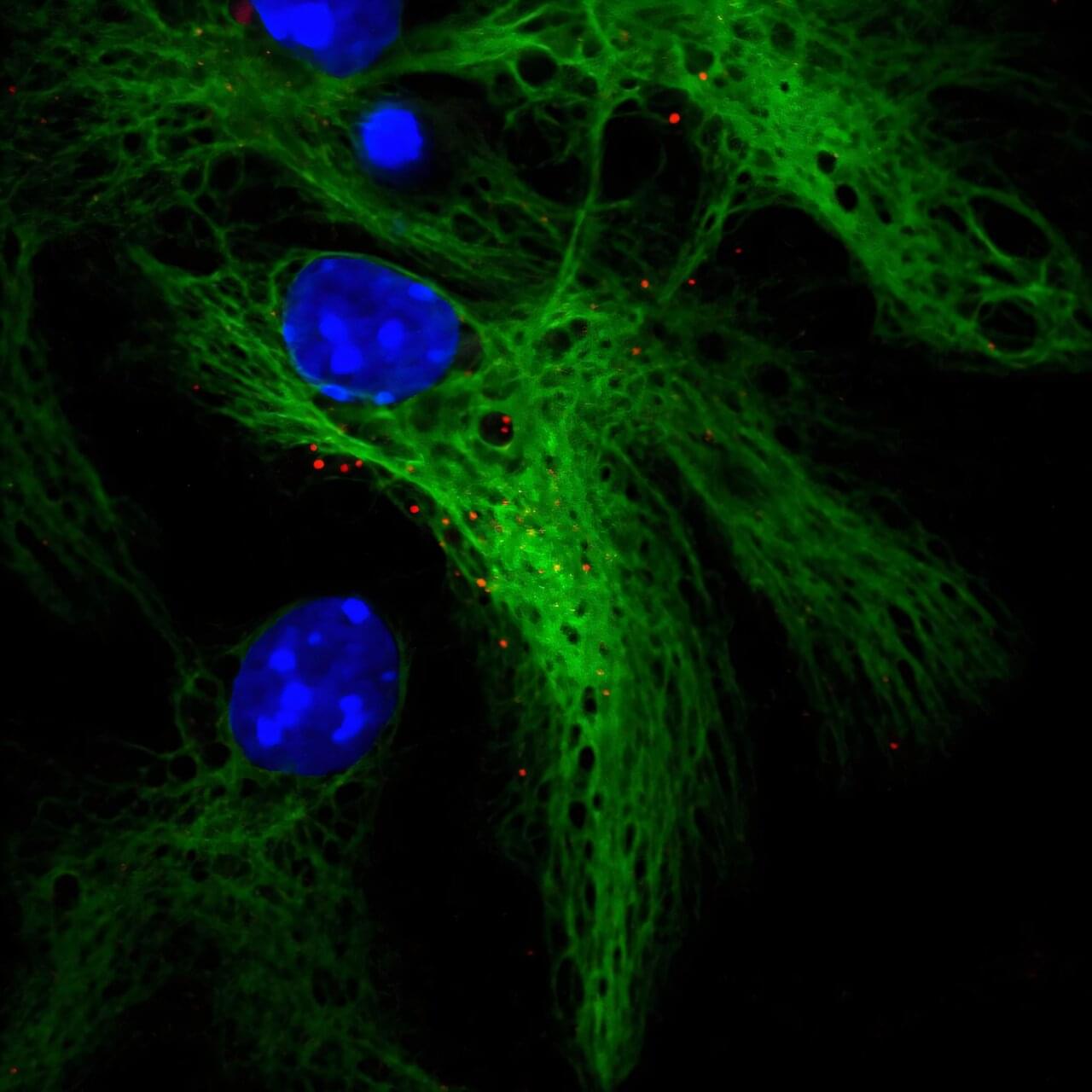
For much of the 20th century it was thought that the adult brain was incapable of regeneration. This view has since shifted dramatically and neurogenesis—the birth of new neurons—is now a widely accepted phenomenon in the adult brain, offering promising avenues for treating many neurological conditions.
One of the main challenges in the field has been identifying neural stem and progenitor cells (NPCs) responsible for generating these new neurons. NPCs are rare, diverse and difficult to isolate from other brain cells due to overlapping molecular signatures. As a result, understanding their biology—and particularly their role in human brain disorders—has remained elusive.
In a study published in Stem Cell Reports, a team led by researchers at Baylor College of Medicine and the Jan and Dan Duncan Neurological Research Institute (Duncan NRI) at Texas Children’s Hospital reveals specific genes that define NPCs.

To build a large-scale quantum computer that works, scientists and engineers need to overcome the spontaneous errors that quantum bits, or qubits, create as they operate.
Scientists encode these building blocks of quantum information to suppress errors in other qubits so that a minority can operate in a way that produces useful outcomes.
As the number of useful (or logical) qubits grows, the number of physical qubits required grows even further. As this scales up, the sheer number of qubits needed to create a useful quantum machine becomes an engineering nightmare.