QuEra has dramatically reduced the error rate in qubits — with its first commercially available machine using this technology launching with 256 physical qubits and 10 logical qubits.


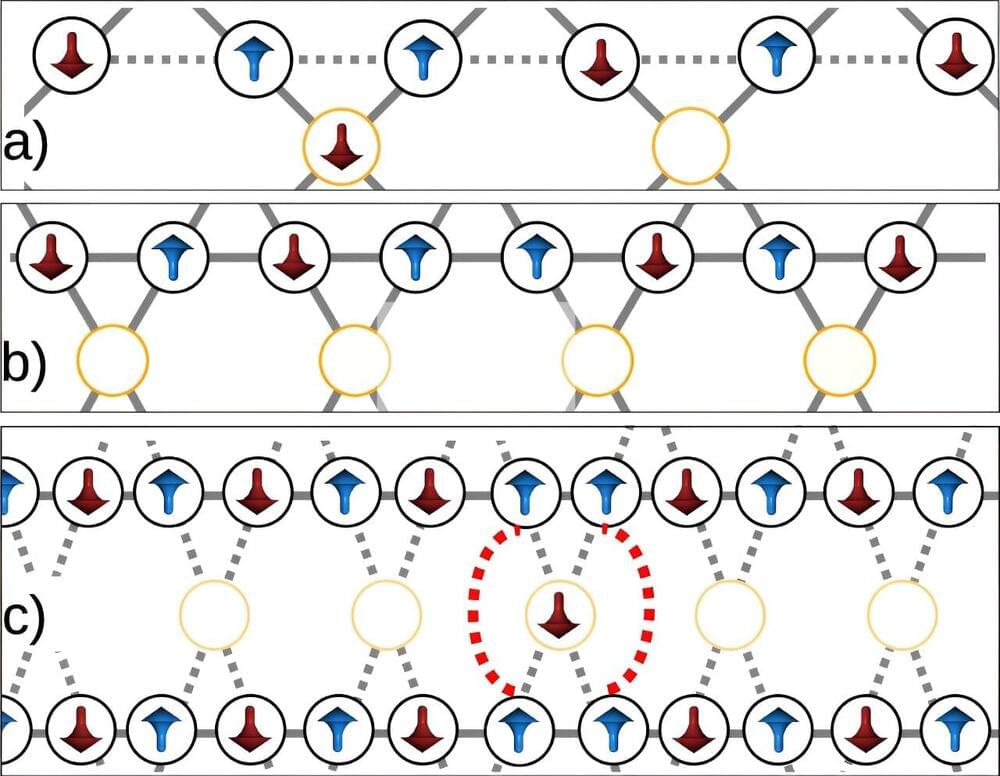
Experimental research conducted by a joint team from Los Alamos National Laboratory and D-Wave Quantum Systems examines the paradoxical role of fluctuations in inducing magnetic ordering on a network of qubits.
Using a D-Wave quantum annealing platform, the team found that fluctuations can lower the total energy of the interacting magnetic moments, an understanding that may help to reduce the cost of quantum processing in devices.
“In this research, rather than focusing on the pursuit of superior quantum computer performance over classical counterparts, we aimed at exploiting a dense network of interconnected qubits to observe and understand quantum behavior,” said Alejandro Lopez-Bezanilla, a physicist in the Theoretical division at Los Alamos.
As demands for computing resources continue to increase rapidly, scientists and engineers are looking for ways to build faster systems for processing information. One possible solution is to use patterns of electron spins, called spin waves, to transfer and process information much more rapidly than in conventional computers. So far, a major challenge has been in manipulating these ultrafast spin waves to do useful work.
In a significant leap forward, researchers from The University of Texas at Austin and MIT have developed a pioneering method to precisely manipulate these ultrafast spin waves using tailored light pulses. Their findings are detailed in two studies in Nature Physics, led by MIT graduate student Zhuquan Zhang, University of Texas at Austin postdoctoral researcher Frank Gao, MIT’s professor of chemistry Keith Nelson and UT Austin assistant professor of physics Edoardo Baldini.
A key component underlying our smartphones, the internet and cloud computing is magnetic data recording technology for storing and retrieving vast amounts of information. This technology hinges on the manipulation of the magnetic spin states (up and down) in ferromagnetic materials, representing the binary bits “0” and “1.” These spins are minuscule magnets, whose alignment determines the material’s magnetic properties.

I believe that the nanotransfection using internal biocomputing will change psychiatric problems because it will physically repair problems with biocomputing rather chemical based computers. Also this could heal the software components aswell of the mind aswell.
Millions of Americans experience symptoms of a mental health condition each year, and the number of people seeking care is trending upward. While a mental health diagnosis may impact an individual’s daily life, it can also have a ripple effect across families, communities and even economies.
Here’s a closer look at the current state of mental health, including how many people experience mental health conditions and which populations are most at risk.
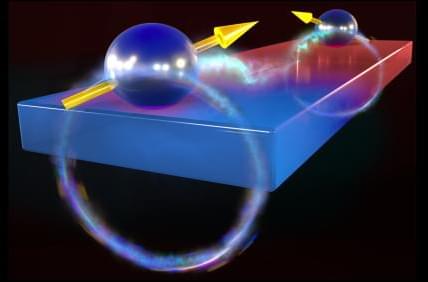
When you push a button to open a garage door, it doesn’t open every garage door in the neighborhood. That’s because the opener and the door are communicating using a specific microwave frequency, a frequency no other nearby door is using.
Researchers from the U.S. Department of Energy’s (DOE) Argonne National Laboratory, the University of Chicago, the University of Iowa and Tohoku University in Japan have begun to develop devices that could use the same principles — sending signals through magnets instead of through the air — to connect individual qubits across a chip, as reported in a new paper published in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences.
“This is a proof of concept, at room temperature, of a scalable, robust quantum technology that uses conventional materials,” said David Awschalom, the Liew Family professor in molecular engineering and physics at the University of Chicago’s Pritzker School of Molecular Engineering; the director of the Chicago Quantum Exchange; the director of Q-NEXT, a DOE National Quantum Information Science Research Center hosted at Argonne; and the principal investigator of the project. “The beauty of this experiment is in its simplicity and its use of well-established technology to engineer and ultimately entangle quantum devices.


In the world of quantum computing, the spotlight often lands on the hardware: qubits, superconducting circuits, and the like. But it’s time to shift our focus to the unsung hero of this tale – the quantum software, the silent maestro orchestrating the symphony of qubits. From turning abstract quantum algorithms into executable code to optimizing circuit designs, quantum software plays a pivotal role.
Here, we’ll explore the foundations of quantum programming, draw comparisons to classical computing, delve into the role of quantum languages, and forecast the transformational impact of this nascent technology. Welcome to a beginner’s guide to quantum software – a journey to the heart of quantum computing.
Quantum vs. Classical Programming: The Core Differences.

How can back-to-back atmospheric rivers impact the economy? This is what a recent study published in Science Advances hopes to address as a team of researchers led by Stanford University investigates the economic toll of back-to-back atmospheric rivers compared to single events. This study holds the potential to help scientists, the public, and city planners better prepare for atmospheric rivers, as they can cause widespread flooding in short periods of time.
For the study, the researchers analyzed data from the Modern-Era Retrospective Analysis for Research and Applications, version 2, (MERRA-2) between 1981 and 2021 and computer algorithms to ascertain the economic impact of atmospheric rivers throughout California. The goal was to ascertain how much worse back-to-back atmospheric rivers were compared to single events. The study’s findings discovered that back-to-back atmospheric rivers caused three times greater economic damage than single events, which is also higher when the first atmospheric river exhibits greater strength.
“Our work really shows that we need to consider the likelihood for multiple, back-to-back events for predicting damages, because damage from multiple events could be far worse than from one event alone,” said Dr. Katy Serafin, who is a coastal scientists and assistant professor in the Department of Geography at the University of Florida and a co-author on the study.