Firefly Aerospace sent a Lockheed Martin payload to the wrong orbit in December, and it is now ‘implementing corrections’ for future missions.
Category: computing – Page 306

Inexpensive device that can harvest energy from a light breeze and store it as electricity
Researchers from Nanyang Technological University in Singapore (NTU Singapore) have created a low-cost tool that can capture power from wind energy as moderate as a light breeze.
The gadget can create a voltage of three volts and energy power of up to 290 microwatts when exposed to winds with speeds as low as 2 meters per second (m/s). This is enough to power a commercial sensor device and allow it to transfer data to a smartphone or computer.
Plasma scientists develop computer programs that could reduce the cost of microchips, stimulate manufacturing
Fashioned from the same element found in sand and covered by intricate patterns, microchips power smartphones, augment appliances and aid the operation of cars and airplanes.
Now, scientists at the U.S. Department of Energy’s (DOE) Princeton Plasma Physics Laboratory (PPPL) are developing computer simulation codes that will outperform current simulation techniques and aid the production of microchips using plasma, the electrically charged state of matter also used in fusion research.
These codes could help increase the efficiency of the manufacturing process and potentially stimulate the renaissance of the chip industry in the United States.

New computer model of lung tissue could herald safer radiotherapy for cancer
An innovative computer model of a human lung is helping scientists simulate, for the first time, how a burst of radiation interacts with the organ on a cell-by-cell level.
This research, carried out at the University of Surrey and GSI Helmholtzzentrum für Schwerionenforschung, Darmstadt, could lead to more targeted treatments for cancer and reduce the damage caused by radiotherapy. The research is published in the journal Communications Medicine.
Dr. Roman Bauer, Senior Lecturer at the University of Surrey, said, “Doctors could one day use our model to choose the right length and strength of radiotherapy—tailored to their patient. This is exciting enough—but others could use our technique to study other organs. This could unlock all kinds of medical knowledge and could be great news for doctors and future patients.”

Challenging Traditional Theories — Physicists Develop New Method To Quantify Quantum Entanglement
Entanglement is a phenomenon in quantum physics where two or more systems become interconnected in a manner that makes it impossible to describe their quantum states separately. When systems interact and become entangled, they exhibit strong correlations. This concept is crucial for quantum computing, as the degree of entanglement directly influences the optimization and efficiency of a quantum computer. The more entangled the systems are, the better the performance of the quantum computer.
A study conducted by researchers affiliated with the Department of Physics at São Paulo State University’s Institute of Geosciences and Exact Sciences (IGCE-UNESP) in Rio Claro, Brazil, tested a novel method of quantifying entanglement and the conditions for its maximization. Applications include optimizing the construction of a quantum computer.
An article on the study is published as a Letter in Physical Review B.
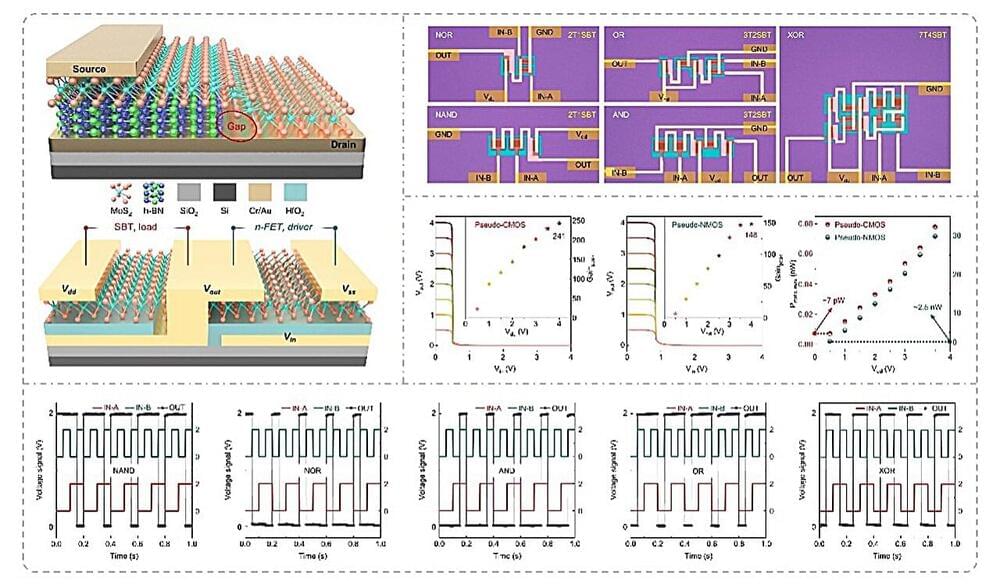
An architecture for sub-picowatt logic computing based on self-biased molybdenum disulfide transistors
The continuous improvement of circuits and electronic components is vital for the development of new technologies with enhanced capabilities and unique characteristics. In recent years, most electronics engineers have been specifically focusing on reducing the size of transistors, while retaining a low power consumption.
Researchers at University of Science and Technology Beijing recently introduced a new pseudo-CMOS architecture based on self-biased molybdenum disulfide transistors. This architecture, outlined in Nature Electronics, could be used to create highly performing inverters, gate circuits, and other device components.
“The development of integrated circuits (ICs) for efficient computing with low power is a global hot topic and a focus of international competition in cutting-edge fields,” Zheng Zhang, co-author of the paper, told Tech Xplore.
Elon Musk shares update on Neuralink’s first human patient
Elon Musk shared an update on Neuralink’s first human patient and their experience with the N1 chip.
The first human Neuralink patient seems to have made a full recovery with no ill effects and is able to control the mouse around the screen just by thinking, said Elon Musk during an apparent on X Spaces.
Musk added that Neuralink continuously observes the patient’s ability to use the N1 brain implant. The patient is currently tasked to click on the mouse button as often as possible.

Neuralink’s first human patient able to control mouse through thinking, Musk says
Feb 20 (Reuters) — The first human patient implanted with a brain-chip from Neuralink appears to have fully recovered and is able to control a computer mouse using their thoughts, the startup’s founder Elon Musk said late on Monday.
“Progress is good, and the patient seems to have made a full recovery, with no ill effects that we are aware of. Patient is able to move a mouse around the screen by just thinking,” Musk said in a Spaces event on social media platform X.
Musk said Neuralink was now trying to get as many mouse button clicks as possible from the patient.
Quantum computing engineers perform multiple control methods in just one atom
Quantum computing engineers at UNSW Sydney have shown they can encode quantum information—the special data in a quantum computer—in four unique ways within a single atom, inside a silicon chip.
The feat could alleviate some of the challenges in operating tens of millions of quantum computing units in just a few square millimeters of a silicon quantum computer chip.
In a paper published in Nature Communications, the engineers describe how they used the 16 quantum ‘states’ of an antimony atom to encode quantum information.