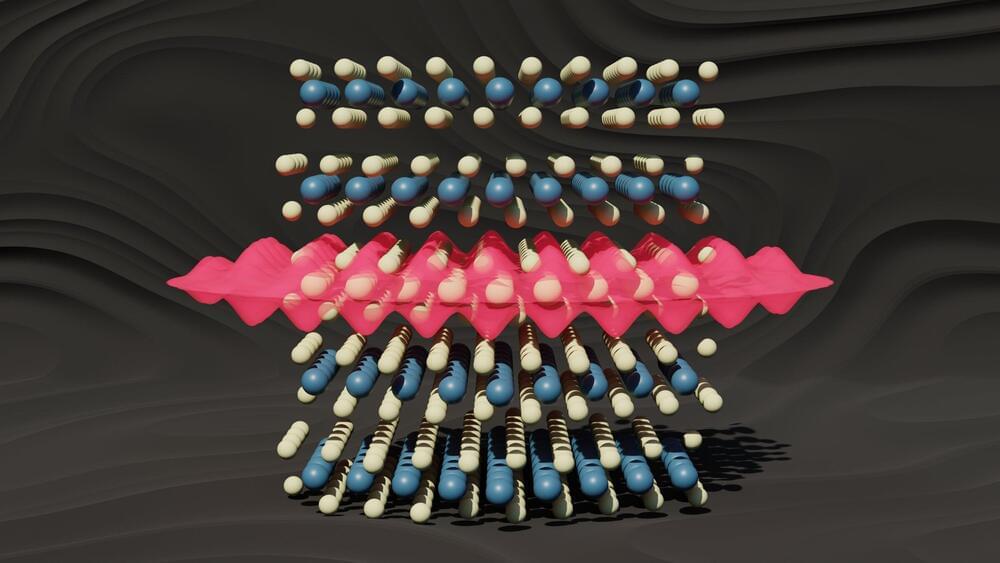
Quantum materials have generated considerable interest for computing applications in the past several decades, but non-trivial quantum properties—like superconductivity or magnetic spin—remain in fragile states.
“When designing quantum materials, the game is always a fight against disorder,” said Robert Hovden, an associate professor of materials science and engineering at the University of Michigan.
Heat is the most common form of disorder that disrupts quantum properties. Quantum materials often only exhibit exotic phenomena at very low temperatures when the atom nearly stops vibrating, allowing the surrounding electrons to interact with one another and rearrange themselves in unexpected ways. This is why quantum computers are currently being developed in baths of liquid helium at −269 °C, or around −450 F. That’s just a few degrees above zero Kelvin (−273.15 °C).