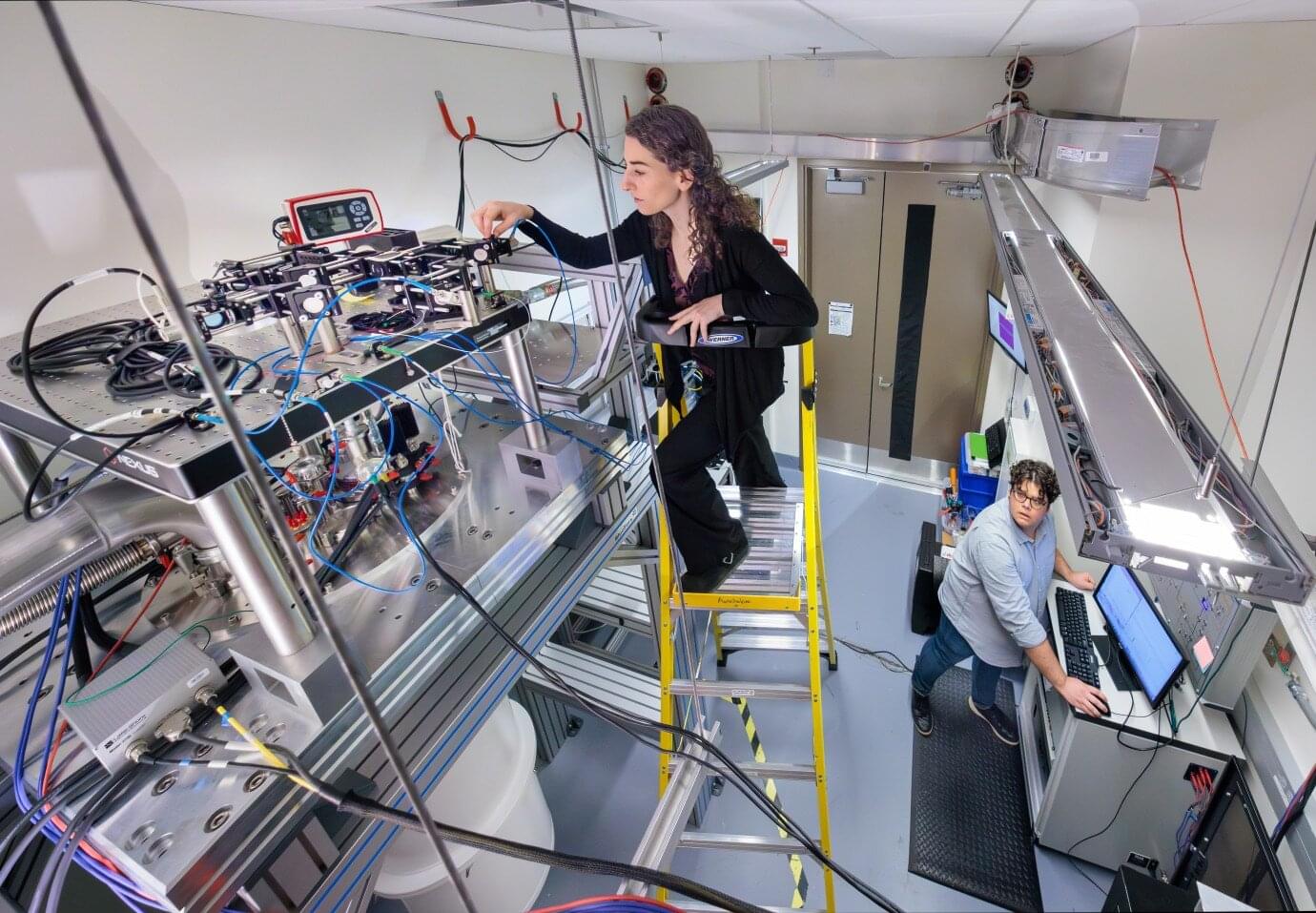
TSMC plans to accelerate US manufacturing, with its new Arizona fab now expected to introduce high-end nodes, such as the A16, significantly ahead of the original timeline.
For those unaware, there’s still a concern by the US administration around TSMC’s operations in the US and Taiwan, and according to Commerce Secretary Howard Lutnick, the USG is now demanding that TSMC produce ‘50% of its total chip capacity’ in America, to ensure that the nation is safeguarded from geopolitical tensions between China and Taiwan. According to a report by the Taiwan Economic Daily, the new Arizona Fab 3 is set to introduce 2nm and A16 in America by 2027, a year ahead of the original timeline.
TSMC is currently pursuing mass production of 4nm in its Arizona facility, and 3nm production lines are also being laid, with production expected to commence by year-end. More importantly, TSMC plans to introduce both 2nm and A16 (1.6nm) with TSMC’s fourth Arizona fab by 2027, which means that relative to Taiwan, the US will just be a year behind, which is a considerable progress in just a span of ‘few months’. In general, TSMC’s 2nm production is slated for next quarter, while A16 will be introduced around H2 2026.