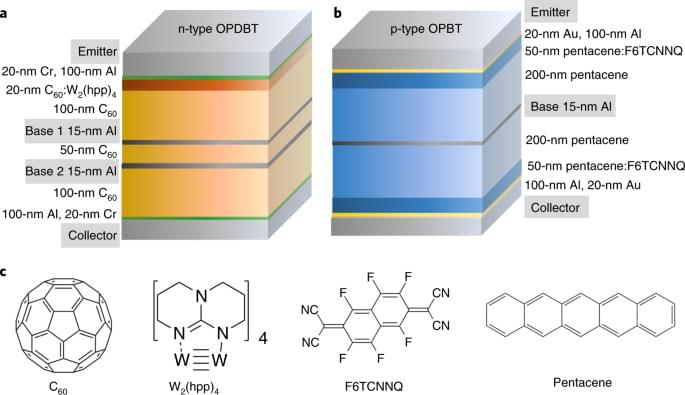
Large-scale control electronics, operating at cryogenic temperatures, are needed to run practical quantum computers. But scaling such electronics means addressing substantial challenges related to power consumption.



Scientists have harnessed many-body physics to transform quantum dots into scalable, stable quantum nodes. By entangling nuclear spins into a ‘dark state,’ they created a quantum register capable of storing and retrieving quantum information with high fidelity. This leap forward brings quantum networks closer to reality, unlocking new possibilities for communication and computing.
For decades, the realm of particle physics has been governed by two major categories: fermions and bosons. Fermions, like quarks and leptons, make up matter, while bosons, such as photons and gluons, act as force carriers. These classifications have long been thought to be the limits of particle behavior. However, a breakthrough has recently changed this understanding.
Researchers have mathematically proven the existence of paraparticles, a theoretical type of particle that doesn’t fit neatly into the traditional fermion or boson categories. These exotic particles were once deemed impossible, defying the conventional laws of physics. Now, thanks to advanced mathematical equations, scientists have demonstrated that paraparticles can exist without violating known physical constraints.
The implications of this discovery could be far-reaching, especially in areas like quantum computing. Paraparticles could offer new possibilities in how we understand the universe at its most fundamental level. While the discovery is still in its early stages, it provides a new tool for physicists to explore more complex systems, potentially unlocking new technologies in the future.
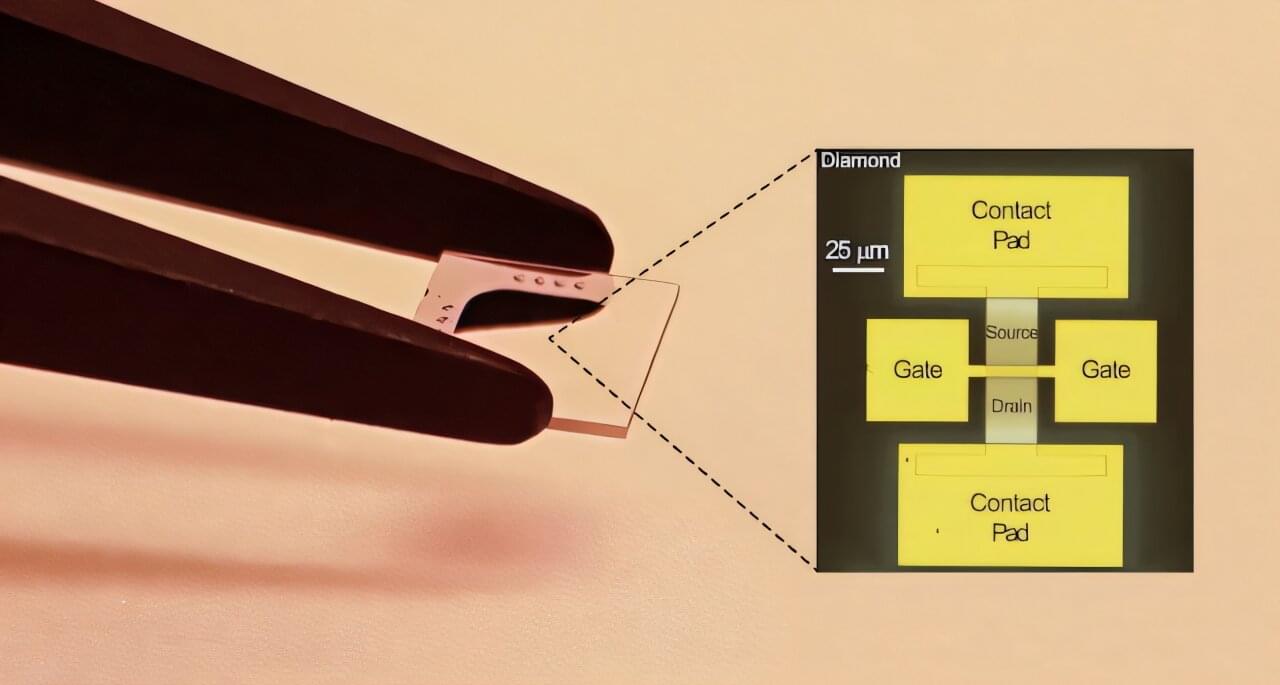
A landmark development led by researchers from the University of Glasgow could help create a new generation of diamond-based transistors for use in high-power electronics.
Their new diamond transistor overcomes the limitations of previous developments in the technology to create a device much closer to being of practical use across a range of industries that rely on high power systems.
The team have found a new way to use diamond as the basis of a transistor that remains switched off by default—a development crucial for ensuring safety in devices that carry a large amount of electrical current when switched on.

A team of engineers, physicists and computer specialists at Canadian company, Xanadu Quantum Technologies Inc., has unveiled what they describe as the world’s first scalable, connected, photonic quantum computer prototype.
In their paper published in the journal Nature, the group describes how they designed and built their modularized quantum computer, and how it can be easily scaled to virtually any desired size.
As scientists around the world continue to work toward the development of a truly useful quantum computer, makers of such machines continue to come up with design ideas. In this new effort, the research team built a quantum computer based on a modular design. Their idea was to build a single basic box using just a few qubits for the simplest of applications. As the need arises, another box can be added, then another and another—with all the boxes working together like a network, as a single computer.
QUT researchers are part of an international group who have explored ways in which organic transistors are being developed for use as wearable health sensors.
The currently available bioelectronic devices, such as pacemakers, that can be embedded with the human body are mostly based on rigid components.
However, the next-generation devices—which are researched and developed by bioelectronic engineers, organic chemists, and materials scientists—will use soft organic materials that allow comfortable wearability as well as efficient monitoring of health.