While significant parts of the globe are already facing significant freshwater scarcity, the need for more freshwater is projected to increase in order to sustain the increasing global population and economic growth and adapt to climate change.
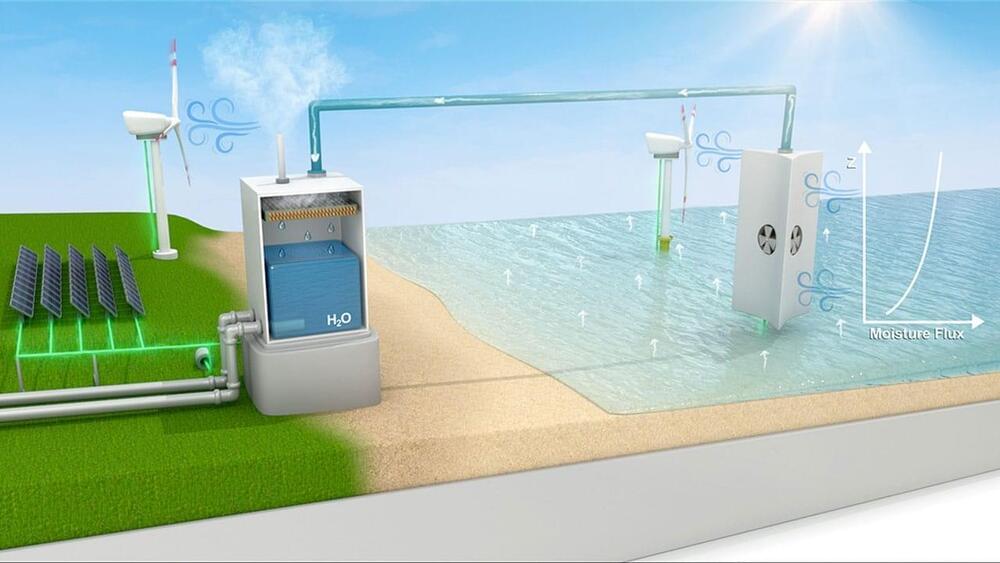
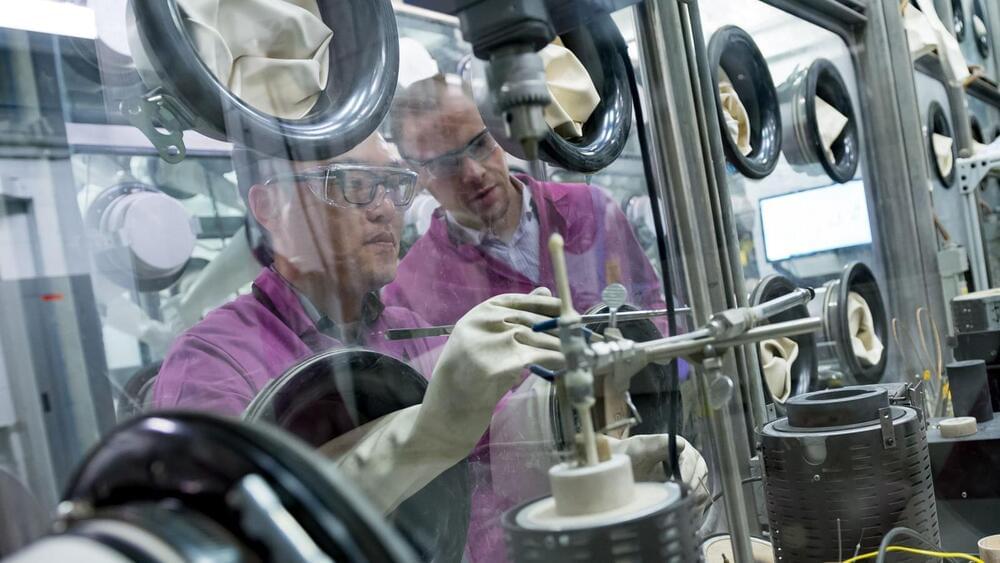
An almost limitless supply of fresh water exists in the form of water vapor above Earth’s oceans, yet remains untapped. Now, researchers at the University of Illinois Urbana-Champaign (UIUC) have proposed a new infrastructure capable of harvesting oceanic water vapor as a solution to limited supplies of fresh water in various locations around the world.
The study evaluated 14 water-stressed locations across the globe for the feasibility of a hypothetical structure capable of capturing water vapor from above the ocean and condensing it into fresh water – and doing so in a manner that will remain feasible in the face of continued climate change.