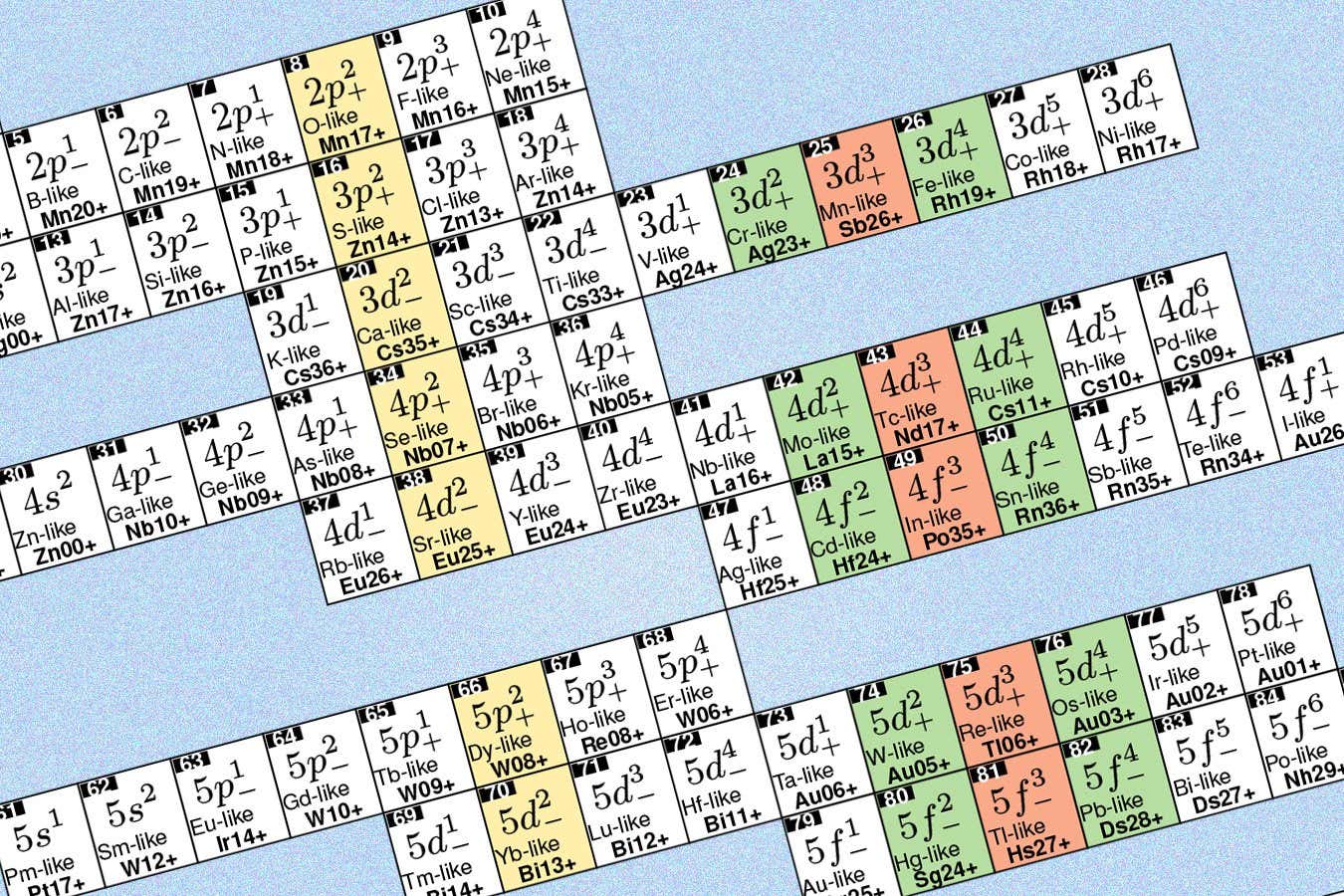
An alternative periodic table of elements focusing on highly charged ions reveals new science that could support the quest for more accurate optical atomic clocks
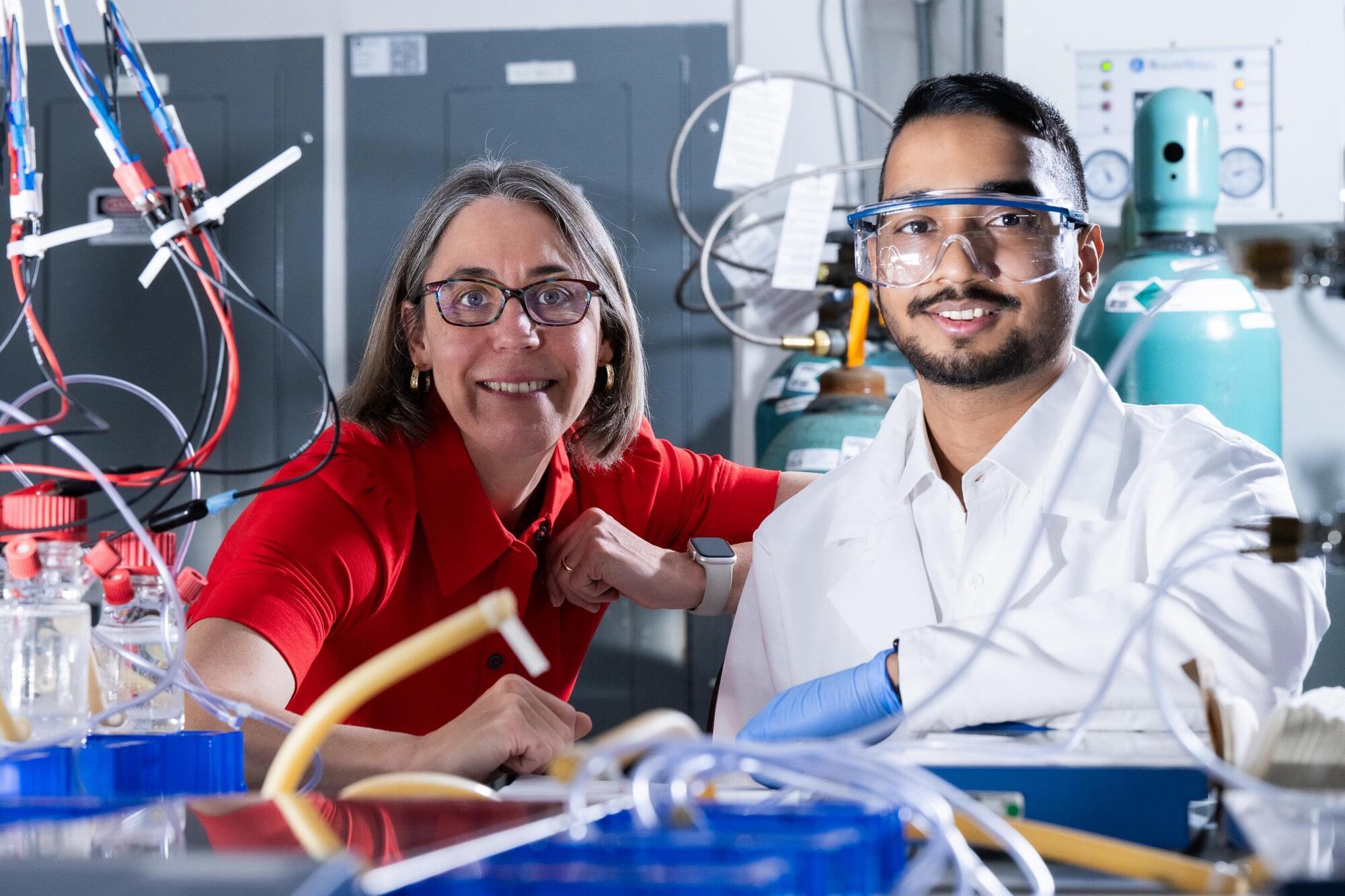


A team led by Rice University bioscientist Caroline Ajo-Franklin has discovered how certain bacteria breathe by generating electricity, using a natural process that pushes electrons into their surroundings instead of breathing on oxygen.
The findings, published in Cell, could enable new developments in clean energy and industrial biotechnology.
By identifying how these bacteria expel electrons externally, the researchers offer a glimpse into a previously hidden strategy of bacterial life. This work, which merges biology with electrochemistry, lays the groundwork for future technologies that harness the unique capabilities of these microscopic organisms.


A Kobe University team was able to edit the DNA of Lactobacillus strains directly without a template from other organisms. This technique is indistinguishable from natural variation and enabled the researchers to create a strain that doesn’t produce diabetes-aggravating chemicals.
Humans have improved the microorganisms we rely on for millennia, selecting variants that are better able to produce wine, yogurt, natto and many other products. More recently, direct genetic modification has emerged as a tool to exert more precise and efficient control over the improvement, but also has drawn much public criticism for often using DNA from unrelated organisms in these modifications. Kobe University bioengineer NISHIDA Keiji says, “As a consequence, using such transgenic techniques is not favorable for food products due to legislations being restrictive and social acceptance being low.”
Nishida and his team have developed a technique that gives even more precise control over the genetic content of a microorganism that does not rely on template DNA from other organisms. He says: “We have invented a DNA base editing technology named ‘Target-AID,’ which is superior to conventional techniques such as ‘CRISPR-Cas9’ in several aspects. For example, CRISPR-Cas9 induces DNA breaks and often causes cell death, while our Target-AID inserts precise point mutations without such breaks.”
Sir Joseph John Thomson (18 December 1856 – 30 August 1940) was an English physicist who received the Nobel Prize in Physics in 1906 “in recognition of the great merits of his theoretical and experimental investigations on the conduction of electricity by gases.” [ 1 ]
In 1897, Thomson showed that cathode rays were composed of previously unknown negatively charged particles (now called electrons), which he calculated must have bodies much smaller than atoms and a very large charge-to-mass ratio. [ 2 ] Thomson is also credited with finding the first evidence for isotopes of a stable (non-radioactive) element in 1913, as part of his exploration into the composition of canal rays (positive ions). His experiments to determine the nature of positively charged particles, with Francis William Aston, were the first use of mass spectrometry and led to the development of the mass spectrograph. [ 2 ] [ 3 ]
Thomson was awarded the 1906 Nobel Prize in Physics for his work on the conduction of electricity in gases. [ 4 ] Thomson was also a teacher, and seven of his students went on to win Nobel Prizes: Ernest Rutherford (Chemistry 1908), Lawrence Bragg (Physics 1915), Charles Barkla (Physics 1917), Francis Aston (Chemistry 1922), Charles Thomson Rees Wilson (Physics 1927), Owen Richardson (Physics 1928) and Edward Victor Appleton (Physics 1947). [ 5 ] Only Arnold Sommerfeld’s record of mentorship offers a comparable list of high-achieving students.

Depression, schizophrenia and other mental health conditions affect 1 in 4 people in their lifetime, but the mechanisms underlying these conditions are poorly understood. New research led by researchers at the University of Bristol has linked the body’s immune response with schizophrenia, Alzheimer’s disease, depression, and bipolar disorder. The study demonstrates mental health conditions might be affected by the whole body as well as changes in the brain. The findings could pave the way for better treatments of some mental health conditions.
The work appears in Molecular Psychiatry.
Most people with depression or schizophrenia are treated with drugs that work on brain chemicals such as serotonin and dopamine. However, one in three people with these conditions do not benefit from these treatments, suggesting that other mechanisms are involved.
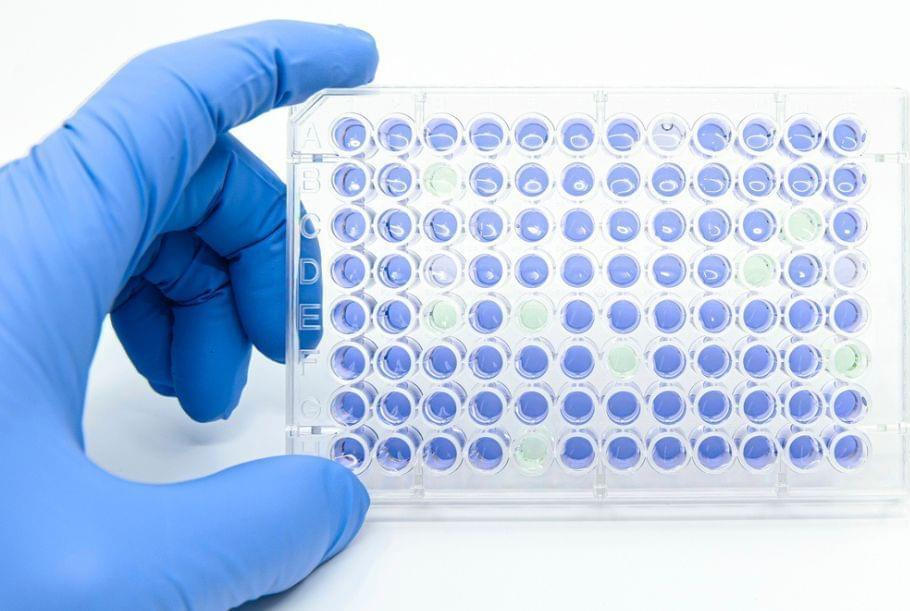
Traditional biochemical methods of studying human gene mutations are often laborious and costly. Now bioengineers at the University of California San Diego have developed a new simple approach to rapidly check on human gene changes and also screen chemicals as potential drugs by turning everyday bacteria into living test tubes.
The researchers published their new study in the April 30 issue of Nature Biomedical Engineering.
Human cells carry thousands of genes, and tiny changes in these genes can cause serious diseases. Usually, scientists study these changes by testing proteins in a test tube or in human cells. But those methods can be slow, expensive and sometimes hard to do.
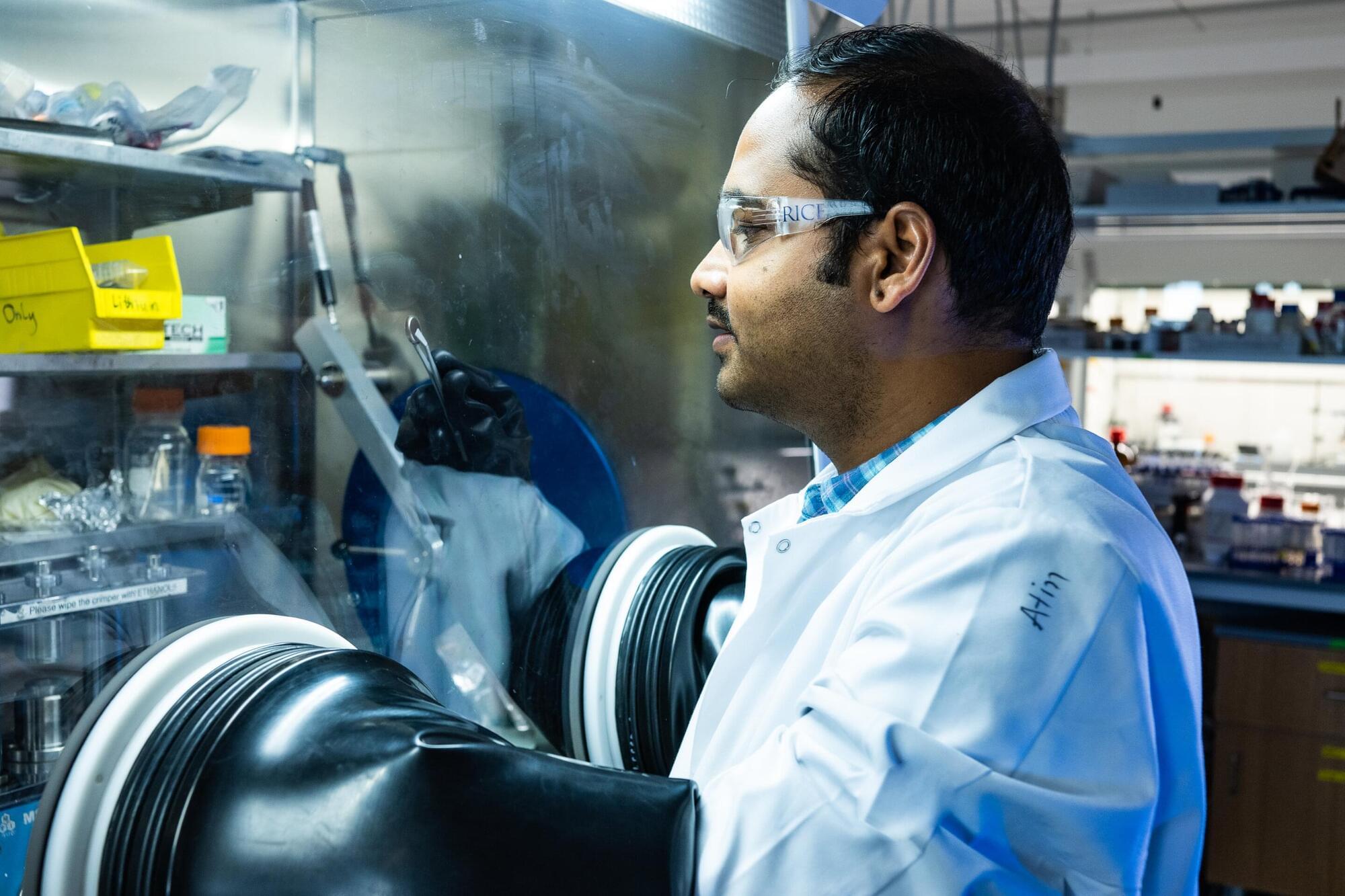

As global demand for electric vehicles and renewable energy storage surges, so does the need for affordable and sustainable battery technologies. A new study has introduced an innovative solution that could impact electrochemical energy storage technologies.
The research is published in the journal Advanced Functional Materials. The work was led by researchers from the Department of Materials Science and NanoEngineering at Rice University, along with collaborators from Baylor University and the Indian Institute of Science Education and Research Thiruvananthapuram.
Using an oil and gas industry’s byproduct, the team worked with uniquely shaped carbon materials —tiny cones and discs—with a pure graphitic structure. These unusual forms produced via scalable pyrolysis of hydrocarbons could help address a long-standing challenge for anodes in battery research: how to store energy with elements like sodium and potassium, which are far cheaper and more widely available than lithium.
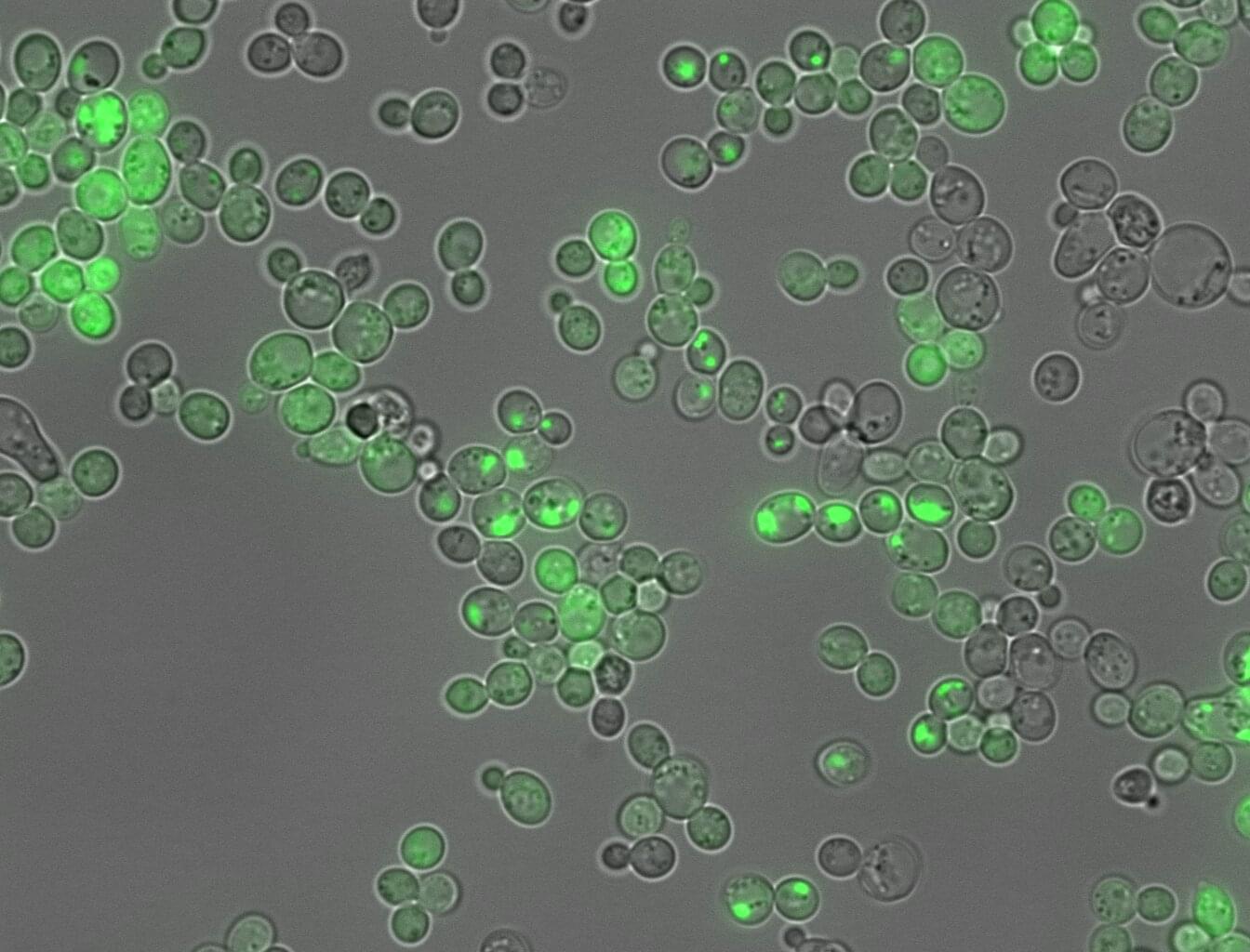
An AI tool has made a step forward in translating the language proteins use to dictate whether they form sticky clumps similar to those linked to Alzheimer’s disease and around fifty other types of human disease. In a departure from typical “black-box” AI models, the new tool, CANYA, was designed to be able to explain its decisions, revealing the specific chemical patterns that drive or prevent harmful protein folding.
The discovery, published in the journal Science Advances, was possible thanks to the largest-ever dataset on protein aggregation created to date. The study gives new insights about the molecular mechanisms underpinning sticky proteins, which are linked to diseases affecting half a billion people worldwide.
Protein clumping, or amyloid aggregation, is a health hazard that disrupts normal cell function. When certain patches in proteins stick to each other, proteins grow into dense fibrous masses that have pathological consequences.
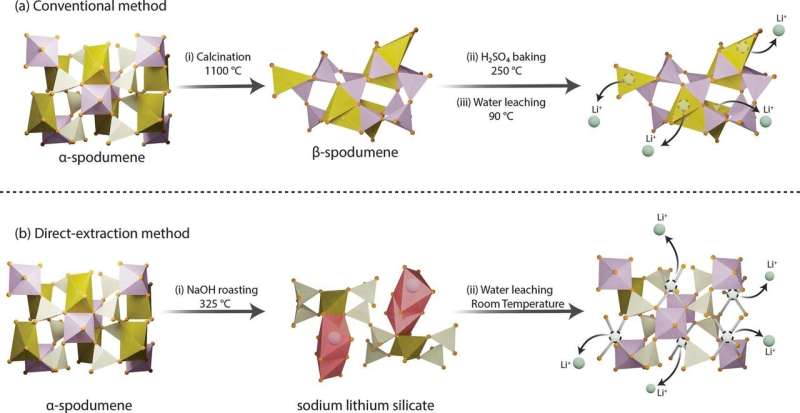
Lightweight lithium metal is a heavy-hitting critical mineral, serving as the key ingredient in the rechargeable batteries that power phones, laptops, electric vehicles and more. As ubiquitous as lithium is in modern technology, extracting the metal is complex and expensive. A new method, developed by researchers at Penn State and recently granted patent rights, enables high-efficiency lithium extraction—in minutes, not hours—using low temperatures and simple water-based leaching.
“Lithium powers the technologies that define our modern lives—from smartphones to electric vehicles—and has applications in grid energy storage, ceramics, glass, lubricants, and even medical and nuclear technologies,” said Mohammad Rezaee, the Centennial Career Development Professor in Mining Engineering at Penn State, who led the team that published their approach in Chemical Engineering Journal.
“But its extraction must also be environmentally responsible. Our research shows that we can extract lithium, and other critical minerals, more efficiently while drastically reducing energy use, greenhouse gas emissions and waste that’s difficult to manage or dispose of.”