Scientists at Europe’s famous particle collider briefly created gold ions from lead in a modern twist on the alchemical goal


Researchers at TUM and TUMint. Energy Research have taken a significant step towards improving solid-state batteries. They developed a new material made of lithium, antimony and scandium that conducts lithium ions more than 30% faster than any previously known material. The work is published in the journal Advanced Energy Materials.
The team led by Prof. Thomas F. Fässler from the Chair of Inorganic Chemistry with a Focus on Novel Materials partially replaced lithium in a lithium antimonide compound with the metal scandium. This creates specific gaps, so-called vacancies, in the crystal lattice of the conductor material. These gaps help the lithium ions to move more easily and faster, resulting in a new world record for ion conductivity.
Since the measured conductivity far exceeded that of existing materials, the team collaborated with the Chair of Technical Electrochemistry under Prof. Hubert Gasteiger at TUM to confirm the result.
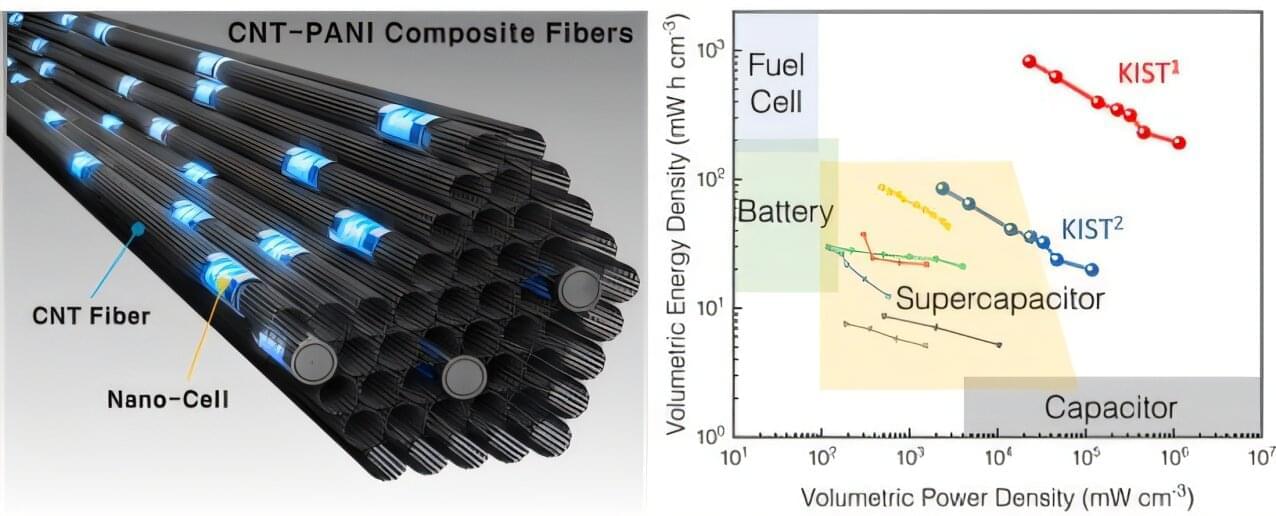
A research team has developed a high-performance supercapacitor that is expected to become the next generation of energy storage devices. With details published in the journal Composites Part B: Engineering, the technology developed by the researchers overcomes the limitations of existing supercapacitors by utilizing an innovative fiber structure composed of single-walled carbon nanotubes (CNTs) and the conductive polymer polyaniline (PANI).
Compared to conventional batteries, supercapacitors offer faster charging and higher power density, with less degradation over tens of thousands of charge and discharge cycles. However, their relatively low energy density limits their use over long periods of time, which has limited their use in practical applications such as electric vehicles and drones.
Researchers led by Dr. Bon-Cheol Ku and Dr. Seo Gyun Kim of the Carbon Composite Materials Research Center at the Korea Institute of Science and Technology (KIST) and Professor Yuanzhe Piao of Seoul National University (SNU), uniformly chemically bonded single-walled carbon nanotubes (CNTs), which are highly conductive, with polyaniline (PANI), which is processable and inexpensive, at the nanoscale.
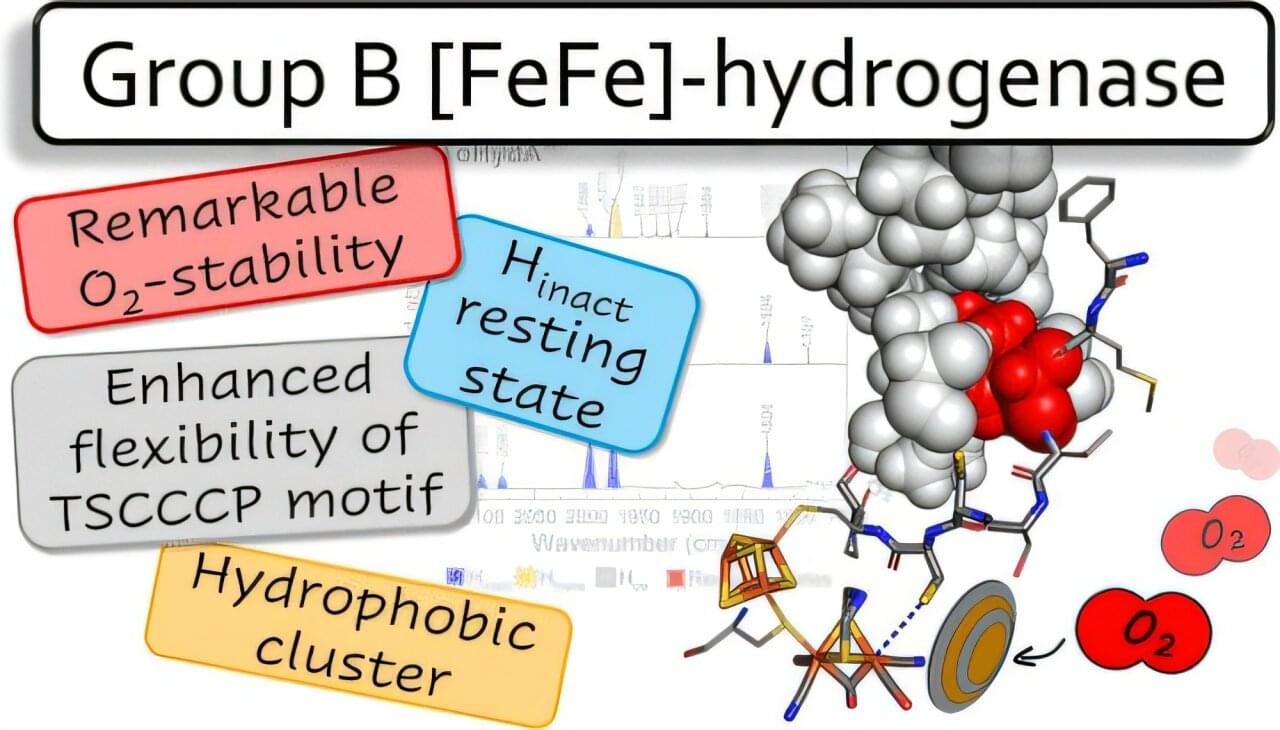
In the absence of air, microorganisms produce hydrogen using an enzyme called [FeFe]-hydrogenase, one of the most efficient hydrogen-producing biocatalysts known and a promising tool for green hydrogen energy. However, these enzymes are rapidly destroyed when exposed to air, which has so far limited their industrial use.
Now, joint efforts led by scientists from the Photobiotechnology group and the Center for Theoretical Chemistry at Ruhr University Bochum, Germany, have isolated a new type of oxygen-stable [FeFe]-hydrogenase and revealed its “tricks” for this oxygen-stability.
The results are published in the Journal of the American Chemical Society.
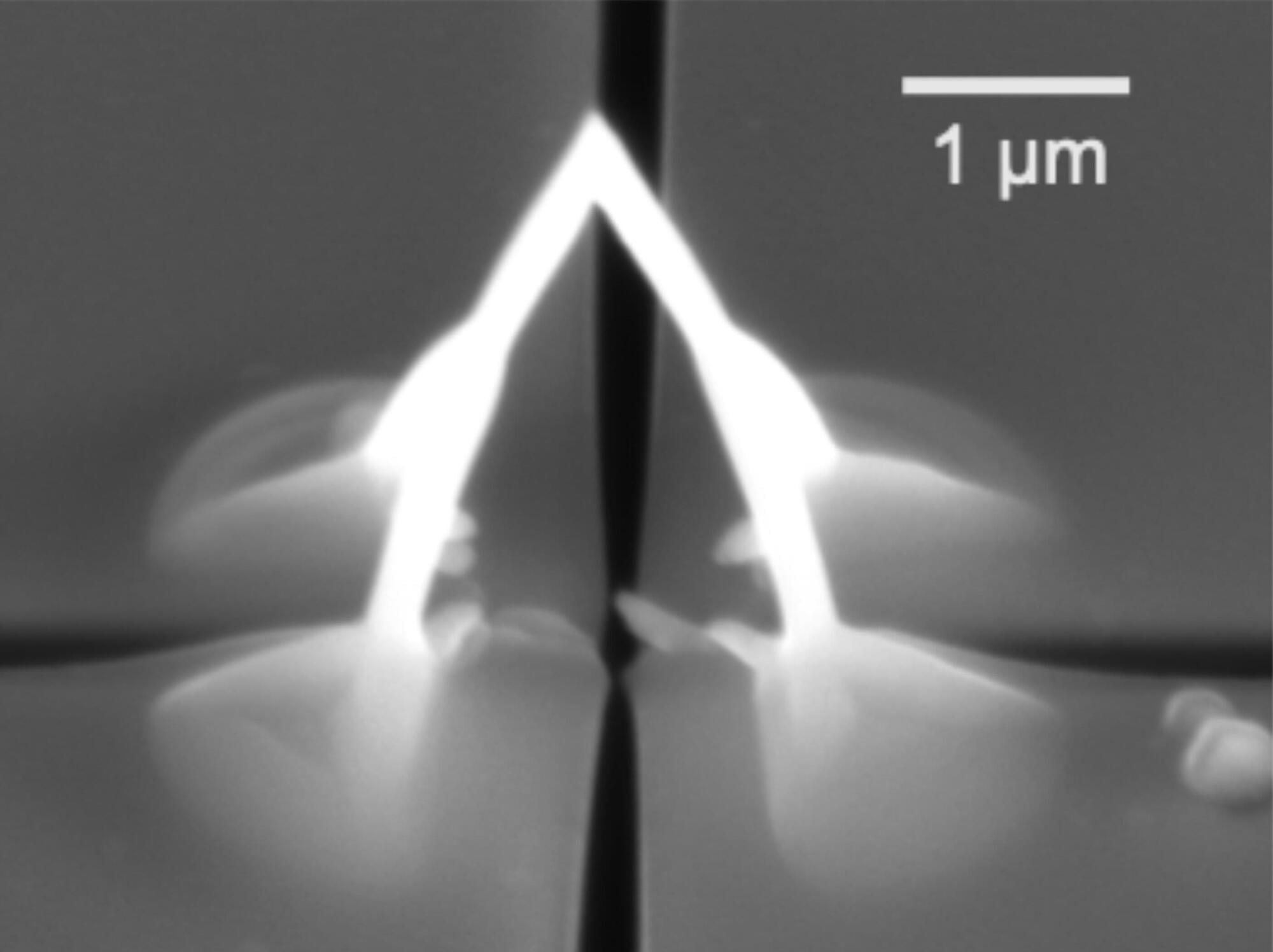
The move from two to three dimensions can have a significant impact on how a system behaves, whether it is folding a sheet of paper into a paper airplane or twisting a wire into a helical spring. At the nanoscale, 1,000 times smaller than a human hair, one approaches the fundamental length scales of, for example, quantum materials.
At these length scales, the patterning of nanogeometries can lead to changes in the material properties itself—and when one moves to three dimensions, there come new ways to tailor functionalities, by breaking symmetries, introducing curvature, and creating interconnected channels.
Despite these exciting prospects, one of the main challenges remains: how to realize such complex 3D geometries, at the nanoscale, in quantum materials? In a new study, an international team led by researchers at the Max Planck Institute for Chemical Physics of Solids have created three-dimensional superconducting nanostructures using a technique similar to a nano-3D printer.
The deconstruction of cellulose is essential for the conversion of biomass into fuels and chemicals. But cellulose, the most abundant renewable polymer on the planet, is extremely recalcitrant to biological depolymerization. Although composed entirely of glucose units, its crystalline microfibrillar structure and association with lignin and hemicelluloses in plant cell walls make it highly resistant to degradation.
As a result, its degradation in nature is slow and requires complex enzymatic systems. The deconstruction of cellulose, which could, among other things, significantly increase the production of ethanol from sugarcane, has been a major technological challenge for decades.
Researchers from the Brazilian Center for Research in Energy and Materials (CNPEM), in partnership with colleagues from other institutions in Brazil and abroad, have just obtained an enzyme that could revolutionize the process of deconstructing cellulose, allowing, among other technological applications, the large-scale production of so-called second-generation ethanol, derived from agro-industrial waste such as sugarcane bagasse and corn straw. The study was published in the journal Nature.

Infrared optoelectronic functional materials are essential for applications in lasers, photodetectors, and infrared imaging, forming the technological backbone of modern optoelectronics. Traditionally, the development of new infrared materials has relied heavily on trial-and-error experimental methods. However, these approaches can be inefficient within the extensive chemical landscape, as only a limited number of compounds can achieve a balance of several critical properties simultaneously.
To tackle this challenge, researchers from the Xinjiang Technical Institute of Physics and Chemistry of the Chinese Academy of Sciences have made significant strides in the machine learning (ML)-assisted discovery of infrared functional materials (IRFMs). The research team has developed a cohesive framework that integrates interpretable ML techniques to facilitate the targeted synthesis of these materials.
The paper is published in the journal Advanced Science.
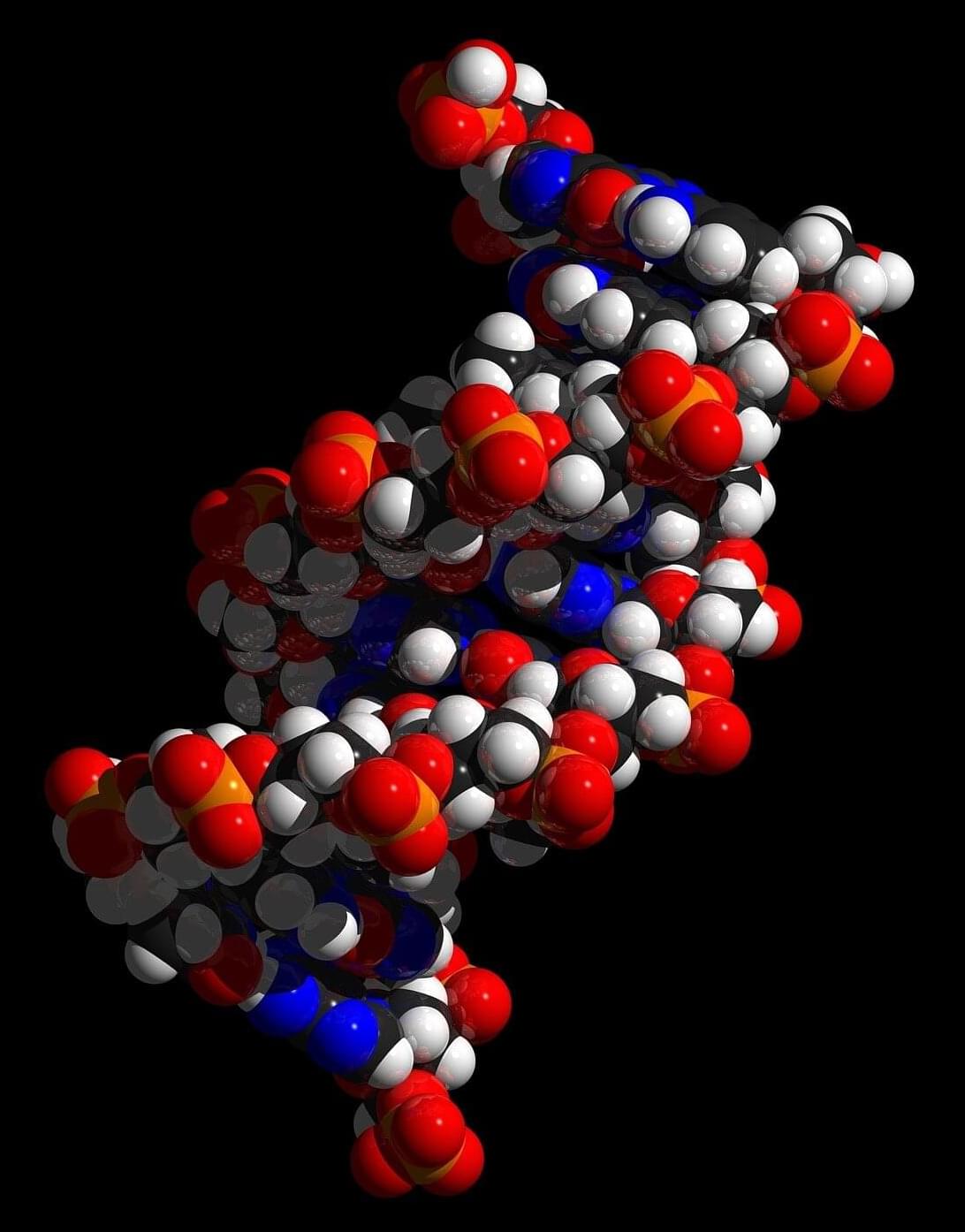
Most biochemistry labs that study DNA isolate it within a water-based solution that allows scientists to manipulate DNA without interacting with other molecules. They also tend to use heat to separate strands, heating the DNA to more than 150°F, a temperature a cell would never naturally reach. By contrast, in a living cell DNA lives in a very crowded environment, and special proteins attach to DNA to mechanically unwind the double helix and then pry it apart.
“The interior of the cell is super crowded with molecules, and most biochemistry experiments are super uncrowded,” said Northwestern professor John Marko. “You can think of extra molecules as billiard balls. They’re pounding against the DNA double helix and keeping it from opening.”

In an experiment reminiscent of the Transformers movie franchise, engineers at Princeton University have created a type of material that can expand, assume new shapes, move and follow electromagnetic commands like a remotely controlled robot even though it lacks any motor or internal gears.
“You can transform between a material and a robot, and it is controllable with an external magnetic field,” said researcher Glaucio Paulino, the Margareta Engman Augustine Professor of Engineering at Princeton.
In an article published April 23 in the journal Nature, the researchers describe how they drew inspiration from the folding art of origami to create a structure that blurs the lines between robotics and materials. The invention is a metamaterial, which is a material engineered to feature new and unusual properties that depend on the material’s physical structure rather than its chemical composition. In this case, the researchers built their metamaterial using a combination of simple plastics and custom-made magnetic composites. Using a magnetic field, the researchers changed the metamaterial’s structure, causing it to expand, move and deform in different directions, all remotely without touching the metamaterial.

Arianna Gleason is an award-winning scientist at the Department of Energy’s SLAC National Accelerator Laboratory who studies matter in its most extreme forms—from roiling magma in the center of our planet to the conditions inside the heart of distant stars. During Fusion Energy Week, Gleason discussed the current state of fusion energy research and how SLAC is helping push the field forward.
Fusion is at the heart of every star. The tremendous pressure and temperature at the center of a star fuses atoms together, creating many of the elements you see on the periodic table and generating an immense amount of energy.
Fusion is exciting, because it could provide unlimited energy to our power grid. We’re trying to replicate fusion energy here on Earth, though it’s a tremendous challenge for science and engineering.