The Virus Zoo is my latest educational blog post! I’ve written up ~1 page ‘cheat sheets’ on the molecular biology of specific viruses. I cover genome, structure, and life cycle. So far, my zoo includes adeno-associated virus (AAV), adenovirus, and herpes simplex virus 1 (HSV-1). However, I plan to add more viruses as time goes on! Some others I would like to incorporate later are coronavirus, HIV, anellovirus, lentivirus, ebolavirus, and MS2 bacteriophage. Feel free to suggest other interesting viruses in the comments! All images were created by me. #virology #molecularbiology #biotechnology #genetherapy #virus #biochemistry #genetics
Genome and Structure:
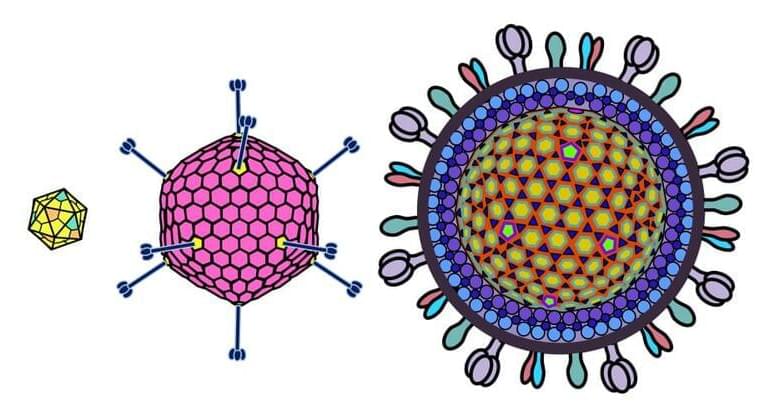
AAV genomes are about 4.7 kb in length and are composed of ssDNA. Inverted terminal repeats (ITRs) form hairpin structures at ends of the genome. These ITR structures are important for AAV genomic packaging and replication. Rep genes (encoded via overlapping reading frames) include Rep78, Rep68, Rep52, Rep40.1 These proteins facilitate replication of the viral genome. As a Dependoparvovirus, additional helper functions from adenovirus (or certain other viruses) are needed for AAVs to replicate.
AAV capsids are about 25 nm in diameter. Cap genes include VP1, VP2, VP3 and are transcribed from overlapping reading frames.2 The VP3 protein is the smallest capsid protein. The VP2 protein is the same as VP3 except that it includes an N-terminal extension with a nuclear localization sequence. The VP1 protein is the same as VP2 except that it includes a further N-terminal extension encoding a phospholipase A2 (PLA2) that facilitates endosomal escape during infection. In the AAV capsid, VP1, VP2, and VP3 are present at a ratio of roughly 1:1:10. It should be noted that this ratio is actually the average of a distribution, not a fixed number.