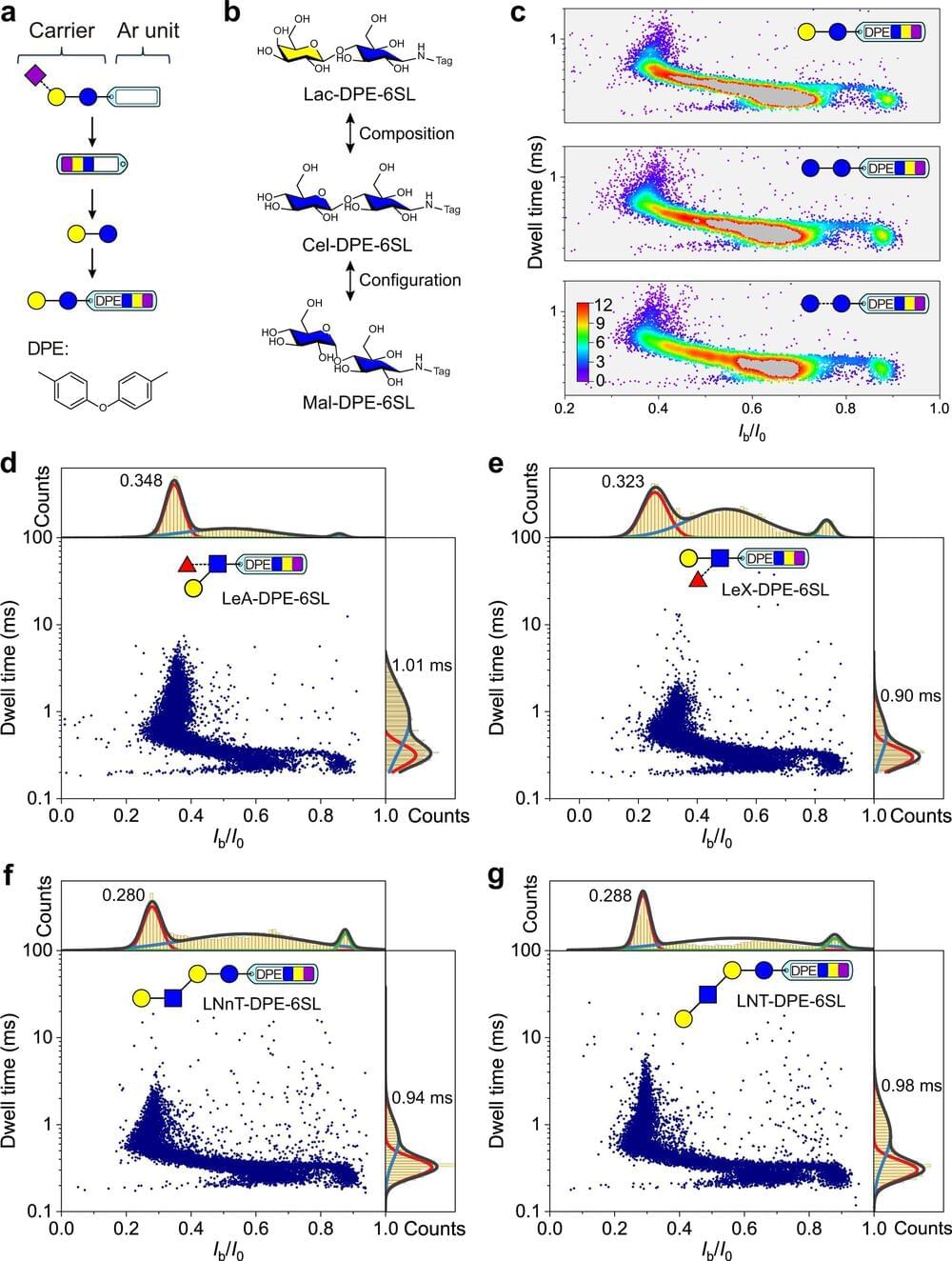
Glycans perform varied and crucial functions in numerous cellular activities. The diverse roles of glycans are matched by their highly complex structures, which derive from differences in composition, branching, regio-and stereochemistry, and modification. This incomparable structural diversity is challenging to the structural analysis of glycans.
Recently, a joint research group led by Prof. Qing Guangyan and Prof. Liang Xinmiao from the Dalian Institute of Chemical Physics (DICP) of the Chinese Academy of Sciences (CAS) has developed a glycan identification method based on nanopore single-molecule sensing through a glycan derivatization strategy. The study was published in Nature Communications on March 28.
Identifying and sequencing glycans using nanopore single-molecule techniques has sparked interest; however, it has achieved little progress over the past dozen years. Only a handful of cases that focused on either high molecular weight polysaccharides or some monosaccharides were reported.