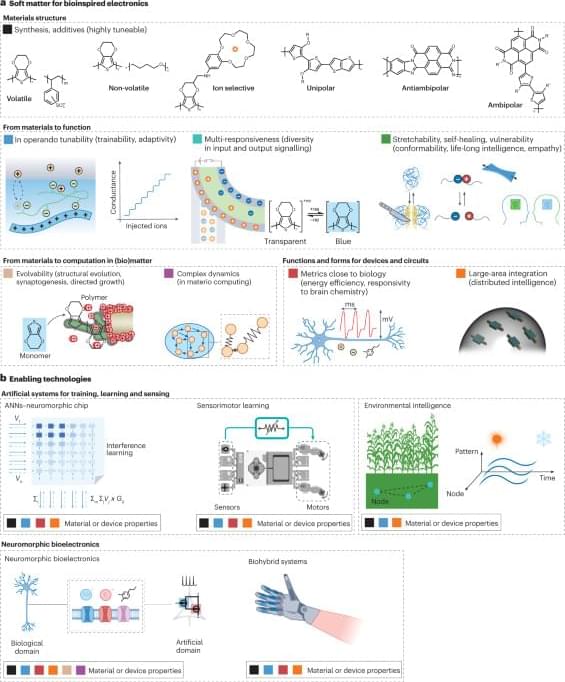
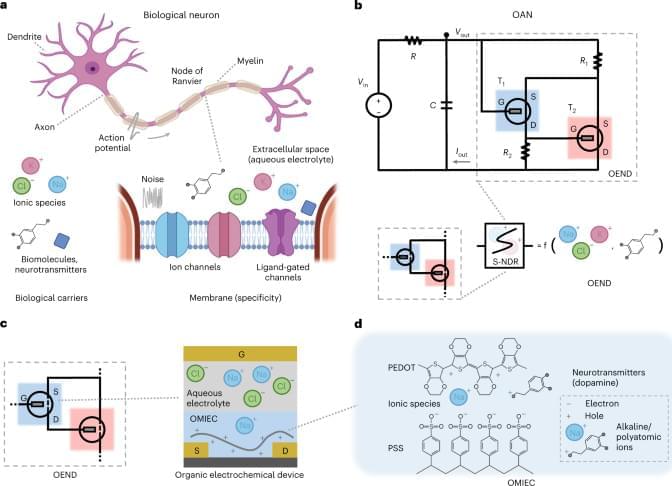
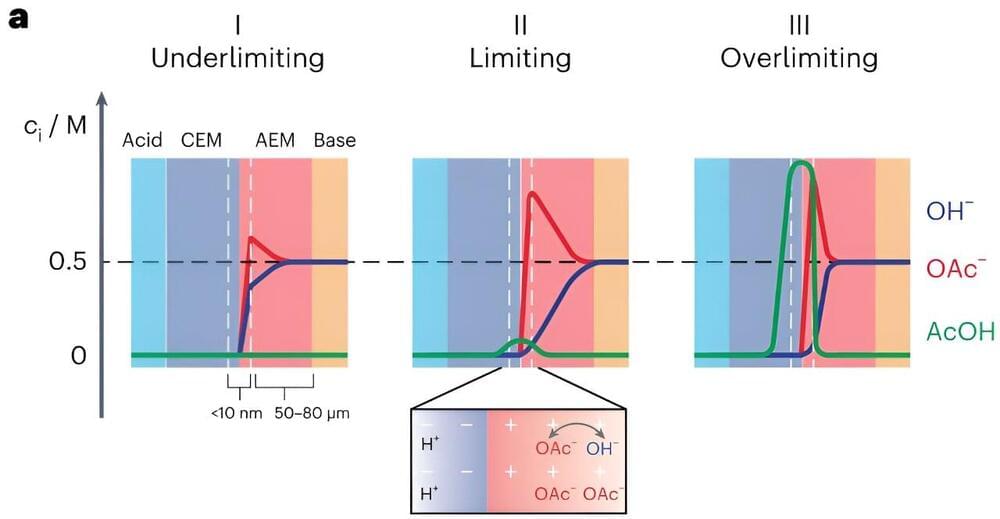
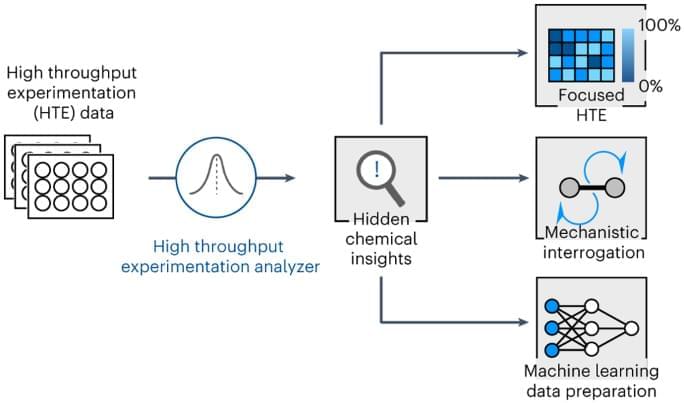
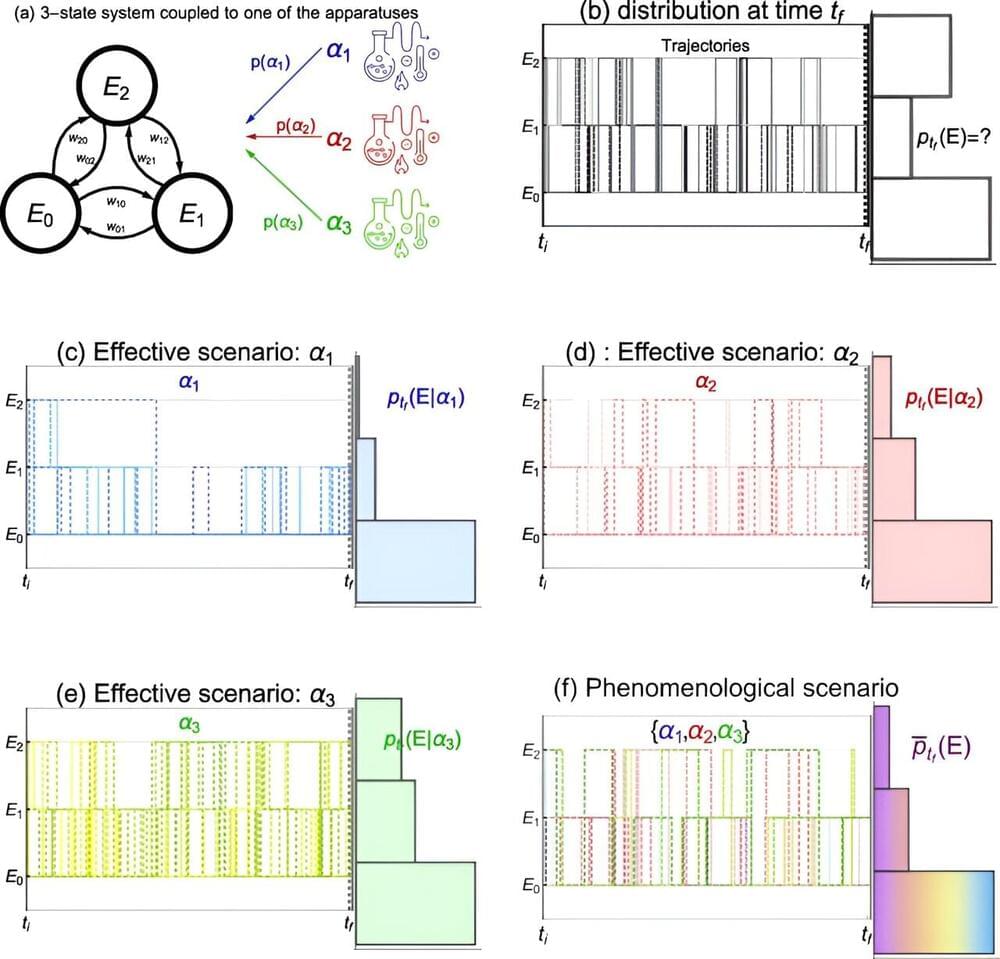
In the vast realm of scientific discovery and technological advancement, there exists a hidden frontier that holds the key to unlocking the mysteries of the universe. This frontier is Pico Technology, a domain of measurement and manipulation at the atomic and subatomic levels. The rise of Pico Technology represents a seismic shift in our understanding of precision measurement and its applications across diverse fields, from biology to quantum computing. Pico Technology, at the intersection of precision measurement and quantum effects, represents the forefront of scientific and technological progress, unveiling the remarkable capabilities of working at the picoscale, offering unprecedented precision and reactivity that are reshaping fields ranging from medicine to green energy.
Unlocking the Picoscale World
At the heart of Pico Technology lies the ability to work at the picoscale, a dimension where a picometer, often represented as 1 × 10^−12 meters, reigns supreme. The term ‘pico’ itself is derived from the Greek word ‘pikos’, meaning ‘very small’. What sets Pico Technology apart is not just its capacity to delve deeper into smaller scales, but its unique ability to harness the inherent physical, chemical, mechanical, and optical properties of materials that naturally manifest at the picoscale.