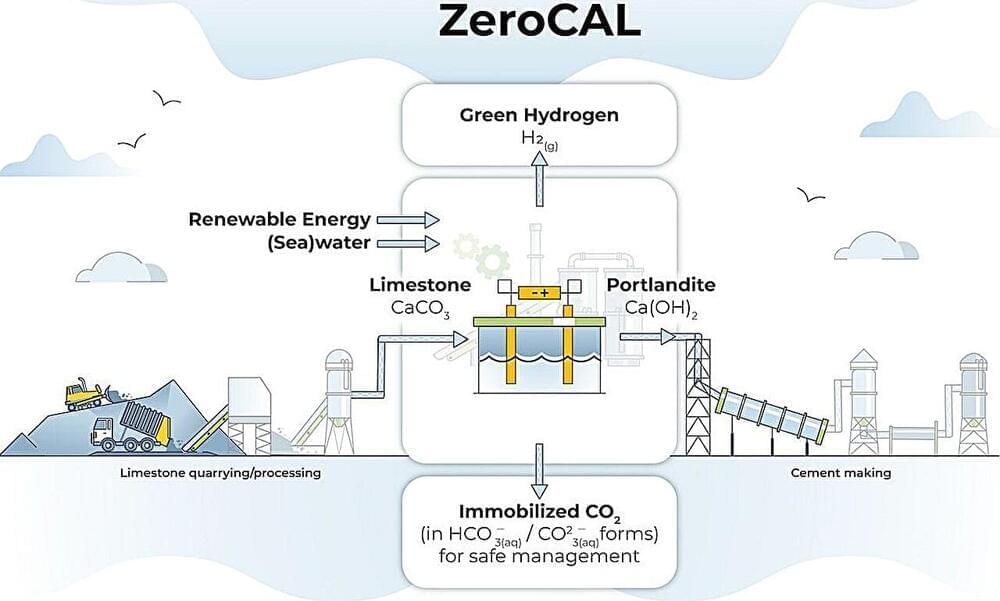
Scientists have synthesized an isotope of the superheavy element livermorium using a novel fusion reaction. The result paves the way for the discovery of new chemical elements.
How and where in the Universe are the chemical elements created? How can we explain their relative abundance? What is the maximum number of protons and neutrons that the nuclear force can bind in a single nucleus? Nuclear physicists and chemists expect to find answers to such questions by creating and studying new elements. But as elements get more and more massive, they become harder and harder to synthesize. The heaviest elements discovered so far were created by bombarding high-atomic-number (high-Z) actinide targets with beams of calcium-48 (48 Ca). This isotope is particularly suited to such experiments because of its peculiar nuclear configuration, in which the number of neutrons and protons are both “magic numbers.” Yet this approach could not produce elements beyond oganesson (proton number, Z = 118).