Increasing energy demands and problems associated with burning fossil fuels have heightened interest in more sustainable energy sources, such as sunlight. But there are still areas where carbon-based fuel remains the standard, such as in the aviation industry. To address this need, scientists have been working to devise a way to use sunlight to generate solar-thermal heating that could then drive the chemical reactions that are needed to make jet fuel with net-zero carbon emissions.
Now, a team at Caltech that is part of a Department of Energy (DOE) Energy Innovation Hub known as the Liquid Sunlight Alliance, or LiSA, has developed such a solar-thermal heating system on a small scale and demonstrated that it can successfully drive an important reaction for jet fuel production.
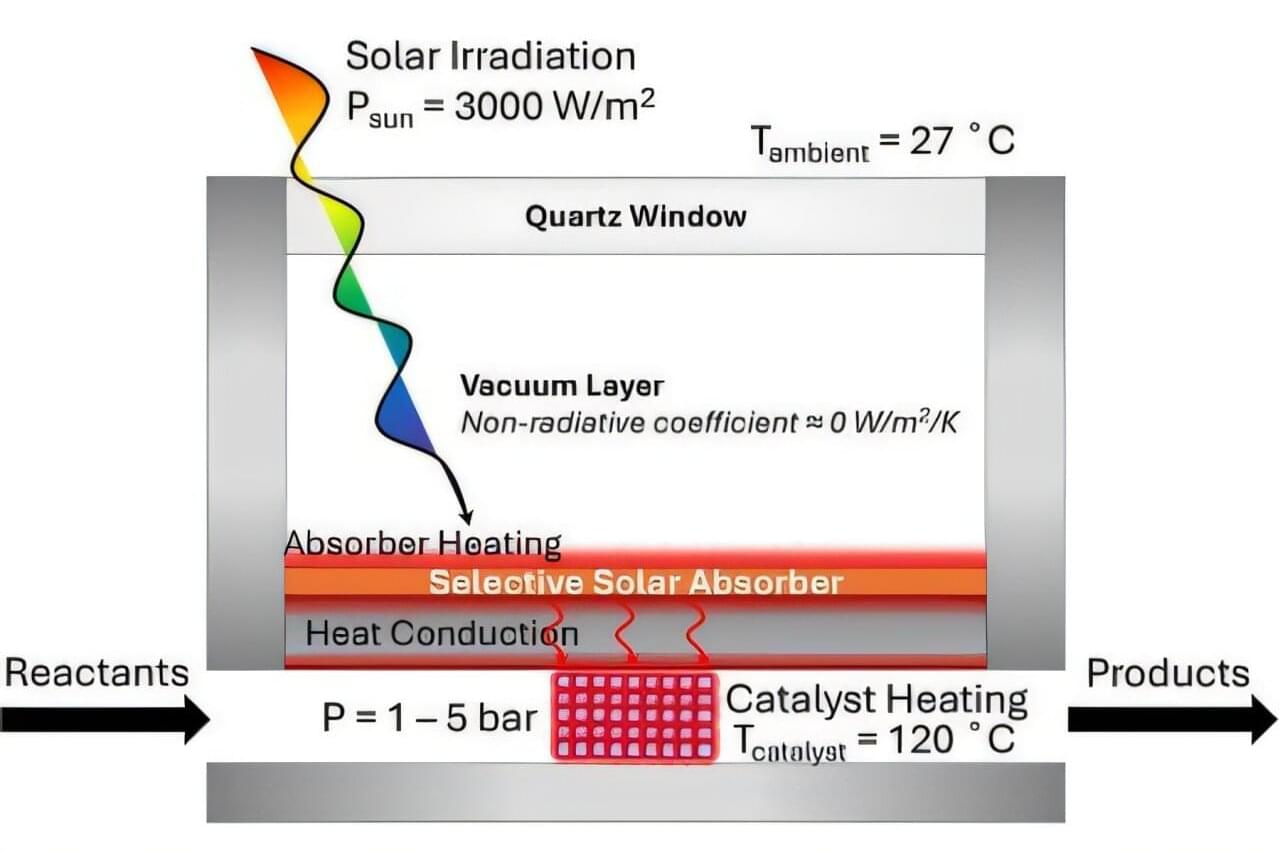
Completely powered by solar energy, the so-called photothermocatalytic reactor incorporates a spectrally selective solar absorber to maximize the generation of solar-thermal heating. The modular design of the reactor takes advantage of current fabrication technologies and existing silicon solar panel production infrastructure.