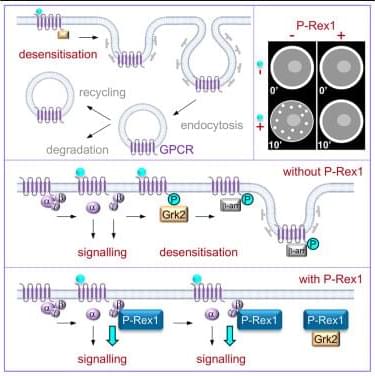
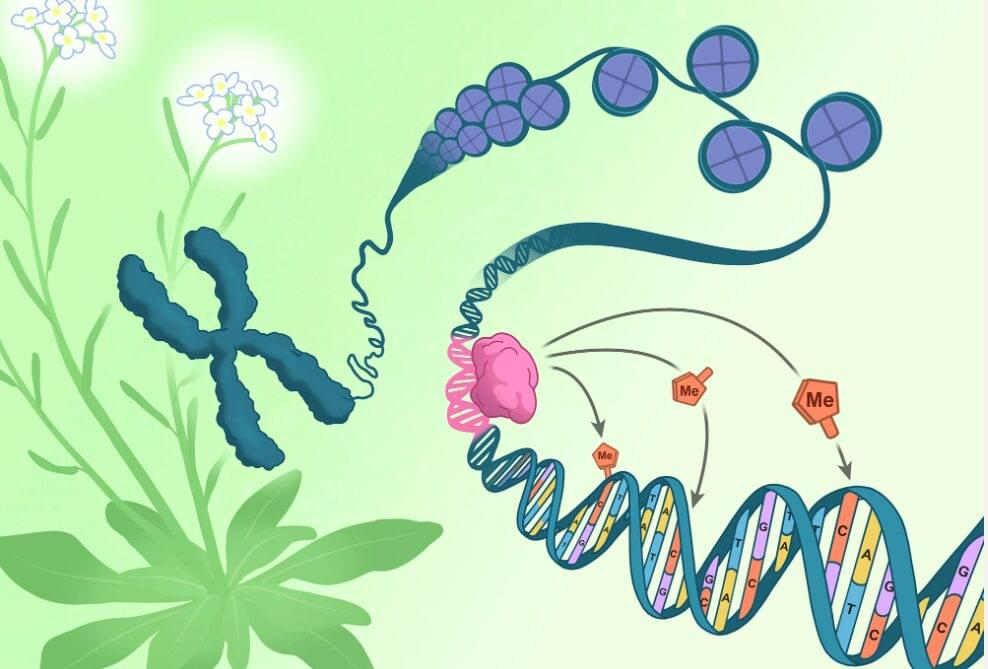
A chromosome pulled from the flowers of Arabidopsis thaliana (green and white) unspools to reveal DNA (blue) coiled around packaging-proteins called histones (purple). The direction of epigenetic changes by genetic features begins as the RIM transcription factor (pink) docks on a corresponding DNA sequence (pink). Once docked, the RIM transcription factor directs methylation machinery to tack methyl groups (orange) onto specific nearby cytosines (orange). Click here for a high-resolution image. Credit: Salk Institute.
All the cells in an organism have the exact same genetic sequence. What differs across cell types is their epigenetics—meticulously placed chemical tags that influence which genes are expressed in each cell. Mistakes or failures in epigenetic regulation can lead to severe developmental defects in plants and animals alike. This creates a puzzling question: If epigenetic changes regulate our genetics, what is regulating them?
Scientists at the Salk Institute have now used plant cells to discover that a type of epigenetic tag, called DNA methylation, can be regulated by genetic mechanisms. This new mode of plant DNA methylation targeting uses specific DNA sequences to tell the methylation machinery where to dock. Prior to this study, scientists had understood only how DNA methylation was regulated by other epigenetic features, so the discovery that genetic features can also guide DNA methylation patterns is a major paradigm shift.