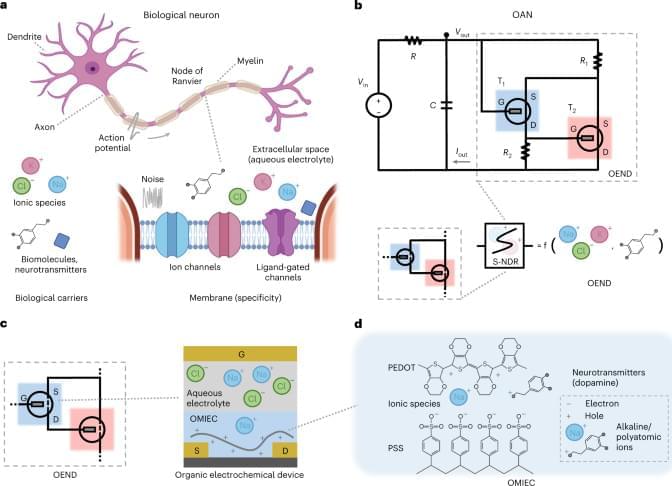
The purpose of the attention schema theory is to explain how an information-processing device, the brain, arrives at the claim that it possesses a non-physical, subjective awareness and assigns a high degree of certainty to that extraordinary claim. The theory does not address how the brain might actually possess a non-physical essence. It is not a theory that deals in the non-physical. It is about the computations that cause a machine to make a claim and to assign a high degree of certainty to the claim. The theory is offered as a possible starting point for building artificial consciousness. Given current technology, it should be possible to build a machine that contains a rich internal model of what consciousness is, attributes that property of consciousness to itself and to the people it interacts with, and uses that attribution to make predictions about human behavior. Such a machine would “believe” it is conscious and act like it is conscious, in the same sense that the human machine believes and acts.
This article is part of a special issue on consciousness in humanoid robots. The purpose of this article is to summarize the attention schema theory (AST) of consciousness for those in the engineering or artificial intelligence community who may not have encountered previous papers on the topic, which tended to be in psychology and neuroscience journals. The central claim of this article is that AST is mechanistic, demystifies consciousness and can potentially provide a foundation on which artificial consciousness could be engineered. The theory has been summarized in detail in other articles (e.g., Graziano and Kastner, 2011; Webb and Graziano, 2015) and has been described in depth in a book (Graziano, 2013). The goal here is to briefly introduce the theory to a potentially new audience and to emphasize its possible use for engineering artificial consciousness.
The AST was developed beginning in 2010, drawing on basic research in neuroscience, psychology, and especially on how the brain constructs models of the self (Graziano, 2010, 2013; Graziano and Kastner, 2011; Webb and Graziano, 2015). The main goal of this theory is to explain how the brain, a biological information processor, arrives at the claim that it possesses a non-physical, subjective awareness and assigns a high degree of certainty to that extraordinary claim. The theory does not address how the brain might actually possess a non-physical essence. It is not a theory that deals in the non-physical. It is about the computations that cause a machine to make a claim and to assign a high degree of certainty to the claim. The theory is in the realm of science and engineering.