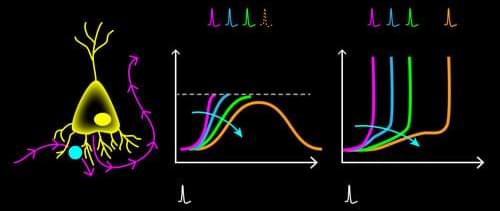
Artificial neural networks (ANNs) have brought about many stunning tools in the past decade, including the Nobel-Prize-winning AlphaFold model for protein-structure prediction [1]. However, this success comes with an ever-increasing economic and environmental cost: Processing the vast amounts of data for training such models on machine-learning tasks requires staggering amounts of energy [2]. As their name suggests, ANNs are computational algorithms that take inspiration from their biological counterparts. Despite some similarity between real and artificial neural networks, biological ones operate with an energy budget many orders of magnitude lower than ANNs. Their secret? Information is relayed among neurons via short electrical pulses, so-called spikes. The fact that information processing occurs through sparse patterns of electrical pulses leads to remarkable energy efficiency.