This man lived inside a self-sustaining glass biosphere for 2 whole years to test drive what life would be like for humans on Mars via NowThis.
Category: biological – Page 204


Don’t Let Robots Pull the Trigger
Ban Killer Robots
“Robotic weapons that target and destroy without human supervision are poised to start a revolution in warfare comparable to the invention of gunpowder or the atomic bomb. The prospect poses a dire threat to civilians—and could lead to some of the bleakest scenarios in which artificial intelligence runs amok. A prohibition on killer robots, akin to bans on chemical and biological weapons, is badly needed. But some major military powers oppose it.”
Weapons that kill enemies on their own threaten civilians and soldiers alike.

Initialization of quantum simulators
Simulating computationally complex many-body problems on a quantum simulator has great potential to deliver insights into physical, chemical and biological systems. Physicists had previously implemented Hamiltonian dynamics but the problem of initiating quantum simulators to a suitable quantum state remains unsolved. In a new report on Science Advances, Meghana Raghunandan and a research team at the institute for theoretical physics, QUEST institute and the Institute for quantum optics in Germany demonstrated a new approach. While the initialization protocol developed in the work was largely independent of the physical realization of the simulation device, the team provided an example of implementing a trapped ion quantum simulator.
Quantum simulation is an emergent technology aimed at solving important open problems relative to high-temperature superconductivity, interacting quantum field theories or many-body localization. A series of experiments have already demonstrated the successful implementation of Hamiltonian dynamics within a quantum simulator—however, the approach can become challenging across quantum phase transitions. In the new strategy, Raghunandan et al. overcame this problem by building on recent advances in the use of dissipative quantum systems to engineer interesting many-body states.
Almost all many-body Hamiltonians of interest remain outside a previously investigated class and therefore require generalization of the dissipative state preparation procedure. The research team therefore presented a previously unexplored paradigm for the dissipative initialization of a quantum simulator by coupling the many-body system performing the quantum simulation to a dissipatively driven auxiliary particle. They chose the energy splitting within the auxiliary particle to become resonant with the many-body excitation gap of the system of interest; described as the difference of the ground-state energy and the energy of the first excited state. During such conditions of resonance, the energy of the quantum simulator could be transferred efficiently to the auxiliary particle for the former to be cooled sympathetically, i.e., particles of one type, cooled particles of another type.
Slime Mold Simulations Map Dark Matter Holding Universe Together
The behavior of one of nature’s humblest creatures is helping astronomers probe the largest structures in the universe.
The single-cell organism, known as slime mold (Physarum polycephalum), builds complex filamentary networks in search of food, finding near-optimal pathways to connect different locations. In shaping the universe, gravity builds a vast cobweb structure of filaments tying galaxies and clusters of galaxies together along faint bridges hundreds of millions of light-years long. There is an uncanny resemblance between the two networks: one crafted by biological evolution, and the other by the primordial force of gravity.
The cosmic web is the large-scale backbone of the cosmos, consisting primarily of the mysterious substance known as dark matter and laced with gas, upon which galaxies are built. Dark matter cannot be seen, but it makes up the bulk of the universe’s material. The existence of a web-like structure to the universe was first hinted at in the 1985 Redshift Survey conducted at the Harvard-Smithsonian Center for Astrophysics. Since those studies, the grand scale of this filamentary structure has grown in subsequent sky surveys. The filaments form the boundaries between large voids in the universe.

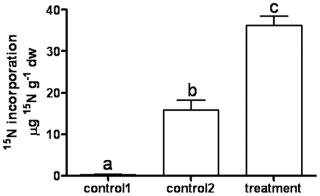
Turning the Table: Plants Consume Microbes as a Source of Nutrients
Editor: Juergen Kroymann, CNRS UMR 8079/Université Paris-Sud, France.
Received: June 7, 2010; Accepted: July 7, 2010; Published: July 30, 2010.
Copyright: © 2010 Paungfoo-Lonhienne et al. This is an open-access distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author and source are credited.


Scientists Linked Artificial and Biological Neurons in a Network—and Amazingly, It Worked
This month, an international team put all of those ingredients together, turning theory into reality.
The three labs, scattered across Padova, Italy, Zurich, Switzerland, and Southampton, England, collaborated to create a fully self-controlled, hybrid artificial-biological neural network that communicated using biological principles, but over the internet.
The three-neuron network, linked through artificial synapses that emulate the real thing, was able to reproduce a classic neuroscience experiment that’s considered the basis of learning and memory in the brain. In other words, artificial neuron and synapse “chips” have progressed to the point where they can actually use a biological neuron intermediary to form a circuit that, at least partially, behaves like the real thing.

Age Reversal Update
An unprecedented human study aims to induce statistically significant and meaningful biological age reversal using multi-model interventions that include metformin, dasatinib, rapamycin, and NAD+ restoration therapy.
By William Faloon.