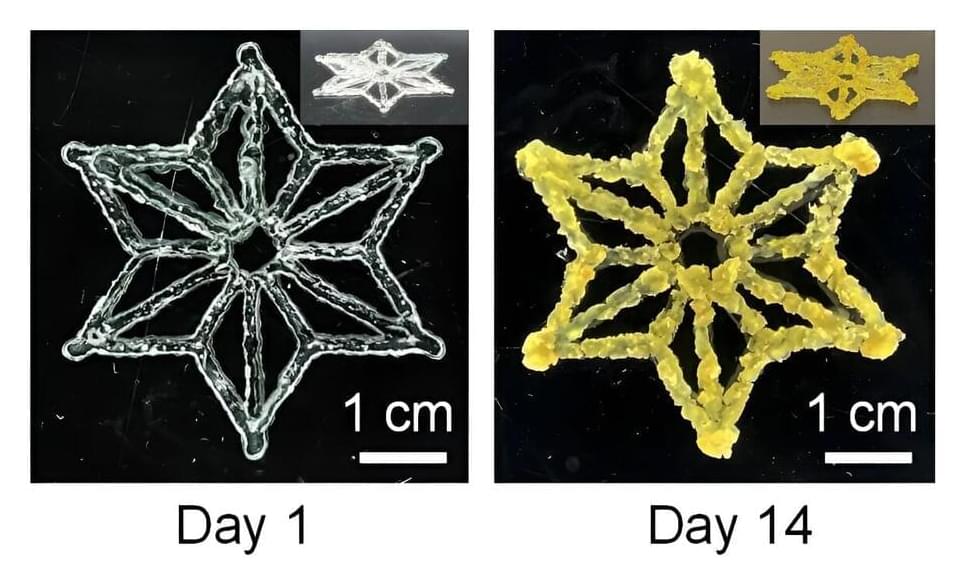
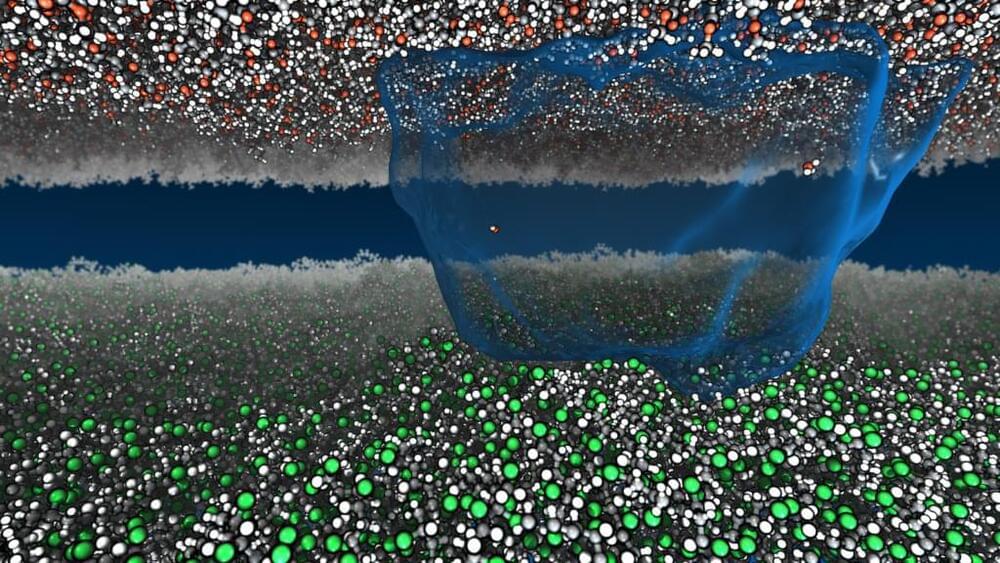
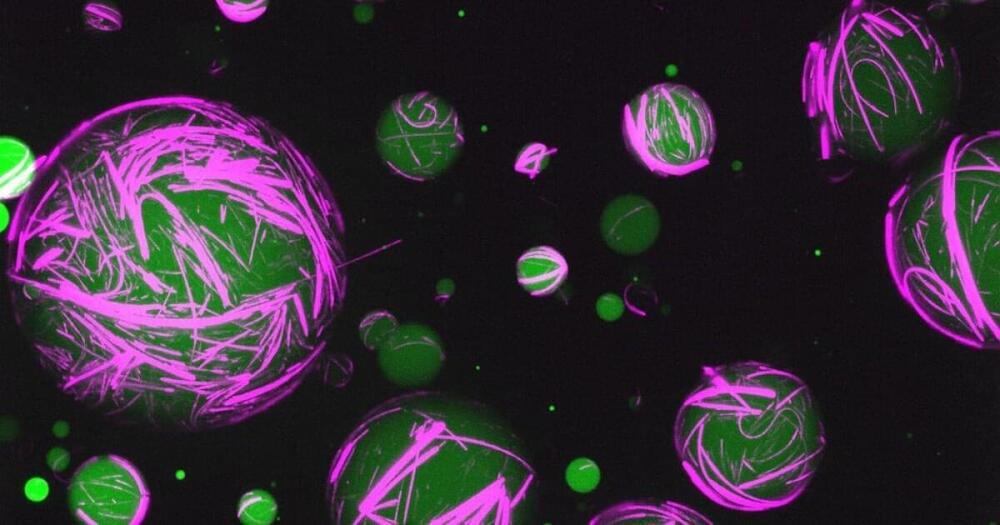
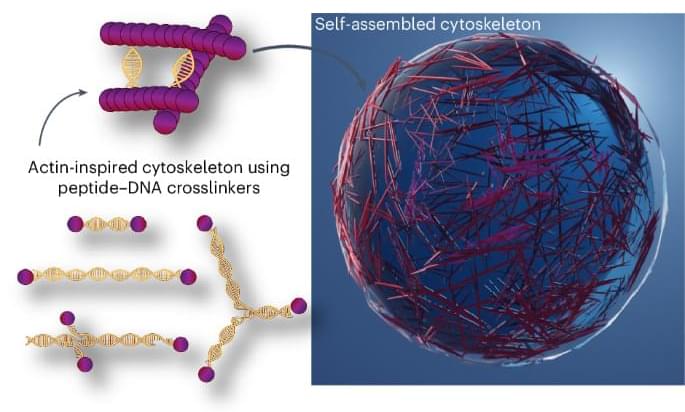
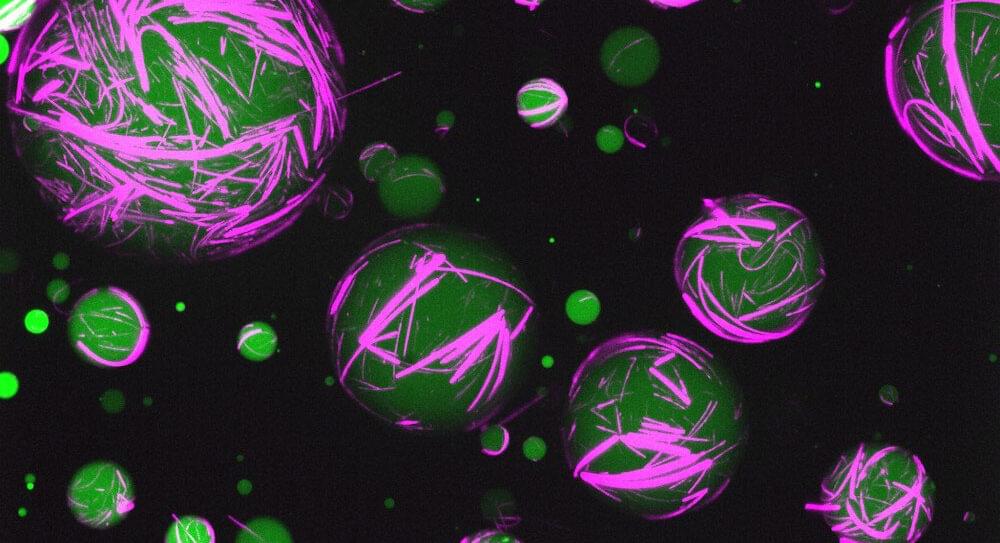
Unlike the rigid skeletons within our bodies, the skeletons within individual cells—cytoskeletons—are changeable, even fluid. And when these cytoskeletons reorganize themselves, they do more than support different cell shapes. They permit different functions.
Little wonder, then, that scientists who build artificial cells hope to create synthetic cytoskeletons that act like natural cytoskeletons. Synthetic cytoskeletons capable of supporting dynamic changes in cell shape and function could enable the development of novel drug delivery systems, diagnostic tools, and regenerative medicine applications.
Synthetic cytoskeletons have incorporated building blocks such as polymers, small molecules, carbon nanotubes, peptides, and DNA nanofilaments. Mostly DNA nanofilaments. Although they offer programmability, they can be hard to fine tune. To get around this difficulty, scientists based at UNC Chapel Hill led by Ronit Freeman, PhD, investigated the relatively unexplored possibilities offered by peptides. Specifically, the scientists engineered artificial cells using a programmable peptide–DNA nanotechnology approach.