Advanced Science is a high-impact, interdisciplinary science journal covering materials science, physics, chemistry, medical and life sciences, and engineering.


Jeff Desjardins, Editor-in-Chief of Visual Capitalist, joins OPTO Sessions to discuss the profound and far-reaching potential of CRISPR and gene editing technology, which he believes could impact fields as diverse as oncology, agriculture and materials science.
On 8 December, the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) approved two cell-based gene therapies for the treatment of sickle cell disease. The decision marked a watershed moment in the history of healthcare, being the first time that gene therapies have won FDA approval.
One of the treatments, Casgevy, is the result of a collaboration between CRISPR Therapeutics [CRSP] and Vertex Pharmaceuticals [VRTX]. The other, Lyfgenia, was developed by bluebird bio [BLUE].
Anthrobots: These remarkable spheroid-shaped multicellular biological robots, or biobots, are not the products of advanced robotics laboratories but are instead born from the inherent potential of adult human somatic progenitor seed cells.
Advanced Science is a high-impact, interdisciplinary science journal covering materials science, physics, chemistry, medical and life sciences, and engineering.
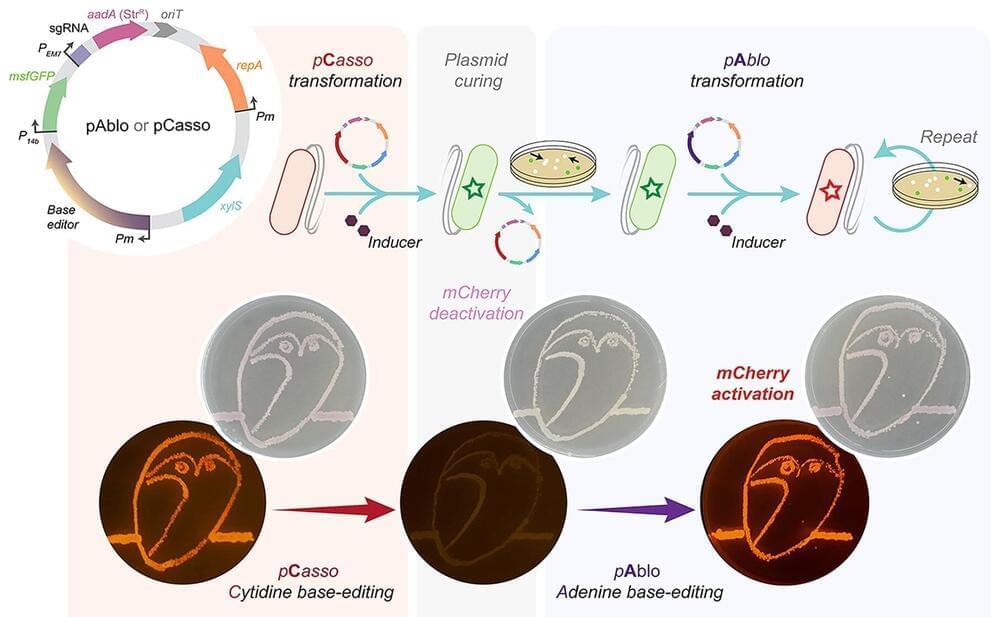
A new CRISPR-Cas toolkit, dubbed “pAblo·pCasso,” is set to transform the landscape of bacterial genome editing, offering unprecedented precision and flexibility in genetic engineering. The new technology, developed by researchers at The Novo Nordisk Foundation Center for Biosustainability (DTU Biosustain), expands the range of genome sites available for base-editing and dramatically accelerates the development of bacteria for a wide range of bioproduction applications.
PAblo·pCasso sets a new standard in CRISPR-Cas technologies. A key innovation is to enable precise and reversible DNA edits within Gram-negative bacteria, a feat not achievable with previous CRISPR systems. The toolkit utilizes specialized fusion enzymes, modified Cas9 coupled with editor modules CBE or ABE, which act like molecular pencils to alter specific DNA nucleotides, thus accurately controlling gene function.
The development of pAblo·pCasso involved overcoming significant challenges. Traditional CRISPR-Cas systems were limited by their need for specific DNA sequences (PAM sequences) near the target site and were less effective in making precise, single-nucleotide changes. pAblo·pCasso transcends these limitations by incorporating advanced Cas-fusion variants that do not require specific PAM sequences, thereby expanding the range of possible genomic editing sites.

When young, these neurons signal fatty tissues to release energy fueling the brain. With age, the line breaks down. Fat cells can no longer orchestrate their many roles, and neurons struggle to pass information along their networks.
Using genetic and chemical methods, the team found a marker for these neurons—a protein called Ppp1r17 (catchy, I know). Changing the protein’s behavior in aged mice with genetic engineering extended their life span by roughly seven percent. For an average 76-year life span in humans, the increase translates to over five years.
The treatment also altered the mice’s health. Mice love to run, but their vigor plummets with age. Reactivating the neurons in elderly mice revived their motivation, transforming them from couch potatoes into impressive joggers.

Big discovery on the patterns of evolution and how it’ll change medicine and even potentially climate change and synthetic biology.
The experts meticulously analyzed the pangenome — a complete set of genes within a species. By deploying a machine learning technique known as Random Forest, and processing data from 2,500 complete genomes of a single bacterial species, the team embarked on a journey to unravel the mysteries of evolutionary predictability.
“The implications of this research are nothing short of revolutionary,” said Professor McInerney, the lead author of the study.
“By demonstrating that evolution is not as random as we once thought, we’ve opened the door to an array of possibilities in synthetic biology, medicine, and environmental science.”
CRISPR pioneer Jennifer Doudna, Ph.D., looks set to continue to push the boundaries of gene editing, as she announces plans to team up with life sciences giant Danaher to create a center focused on generating new therapies for rare and other diseases.
The center, which will be based at the headquarters of Doudna’s own Innovative Genomics Institute (IGI) and referred to as the Danaher-IGI Beacon for CRISPR Cures, “aims to use CRISPR-based gene editing to permanently address hundreds of diseases with a unified research, development and regulatory approach,” according to a Jan. 9 release from Danaher.
An unexpected genetic discovery in wheat has led to opportunities for the metabolic engineering of versatile compounds with the potential to improve its nutritional qualities and resilience to disease.
Researchers in the Osbourn group at the John Innes Centre have been investigating biosynthetic gene clusters in wheat – groups of genes that are co-localized on the genome and work together to produce specific molecules.

Background: The Promise of Prime Editing
Prime editing is a promising technology for changing genomic deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) that has the potential to be used to cure genetic diseases in individuals. Prime editors are proteins that can replace a specific deoxyribonucleic acid sequence with another. PE systems necessitate three distinct nucleic acid hybridizations and are not dependent on double-strand deoxyribonucleic acid breaks or donor deoxyribonucleic acid templates.
Researchers must devise efficient and safe techniques to deliver prime editors in tissues in the in vivo settings to fulfill PE’s objective. While viral delivery techniques such as adenoviruses and adeno-associated viruses (AAVs) can transport PE in vivo, non-viral delivery techniques like lipid nanoparticles can sidestep these concerns by packaging PEs as temporarily expressing messenger ribonucleic acids.