Circa 2020 Immortality of the heart and heart regeneration.
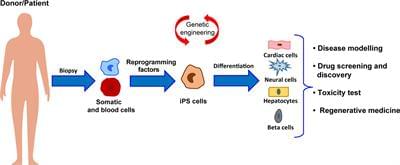
Cardiovascular diseases represent the major cause of morbidity and mortality worldwide. Multiple studies have been conducted so far in order to develop treatments able to prevent the progression of these pathologies. Despite progress made in the last decade, current therapies are still hampered by poor translation into actual clinical applications. The major drawback of such strategies is represented by the limited regenerative capacity of the cardiac tissue. Indeed, after an ischaemic insult, the formation of fibrotic scar takes place, interfering with mechanical and electrical functions of the heart. Hence, the ability of the heart to recover after ischaemic injury depends on several molecular and cellular pathways, and the imbalance between them results into adverse remodeling, culminating in heart failure. In this complex scenario, a new chapter of regenerative medicine has been opened over the past 20 years with the discovery of induced pluripotent stem cells (iPSCs). These cells share the same characteristic of embryonic stem cells (ESCs), but are generated from patient-specific somatic cells, overcoming the ethical limitations related to ESC use and providing an autologous source of human cells. Similarly to ESCs, iPSCs are able to efficiently differentiate into cardiomyocytes (CMs), and thus hold a real regenerative potential for future clinical applications. However, cell-based therapies are subjected to poor grafting and may cause adverse effects in the failing heart. Thus, over the last years, bioengineering technologies focused their attention on the improvement of both survival and functionality of iPSC-derived CMs. The combination of these two fields of study has burst the development of cell-based three-dimensional (3D) structures and organoids which mimic, more realistically, the in vivo cell behavior. Toward the same path, the possibility to directly induce conversion of fibroblasts into CMs has recently emerged as a promising area for in situ cardiac regeneration. In this review we provide an up-to-date overview of the latest advancements in the application of pluripotent stem cells and tissue-engineering for therapeutically relevant cardiac regenerative approaches, aiming to highlight outcomes, limitations and future perspectives for their clinical translation.
Cardiovascular diseases represent the major cause of morbidity and mortality worldwide, accounting for 31% of all deaths (Organization WH 2016). Myocardial infarction (MI) is associated with necrosis of the cardiac tissue due to the occlusion of the coronary arteries, a condition that irrevocably diminishes oxygen and nutrient delivery to the heart (Thygesen et al., 2007). While effective therapies, including surgical approaches, are currently used to treat numerous cardiac disorders, such as valvular or artery diseases, available therapeutic treatments for the damaged myocardium are still very limited and poorly effective. Furthermore, after an ischaemic insult, the formation of fibrotic scar takes place, interfering with mechanical and electrical functions of the cardiac tissue (Talman and Ruskoaho, 2016).