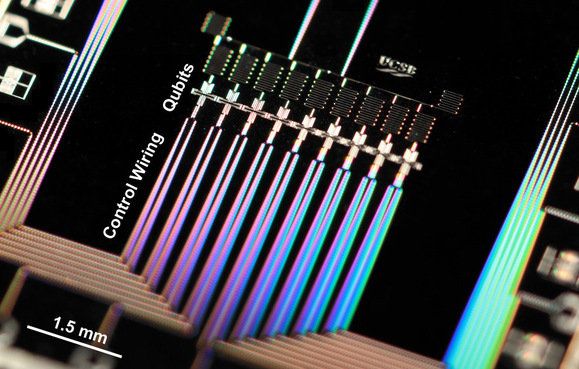
Any technology with the word “quantum” in the name is by nature impossible for lay people to understand and even difficult for scientists to get their arms fully around. However, though its workings are mysterious, quantum science offers very useful everyday tools.
There has been a race for quantum computing for years. Part of the reason is that these devices will leave today’s computers in the dust. The other element is that planners see that current computing technology is reaching its growth limits. Quantum computing is the key to the future to them, not science fiction.
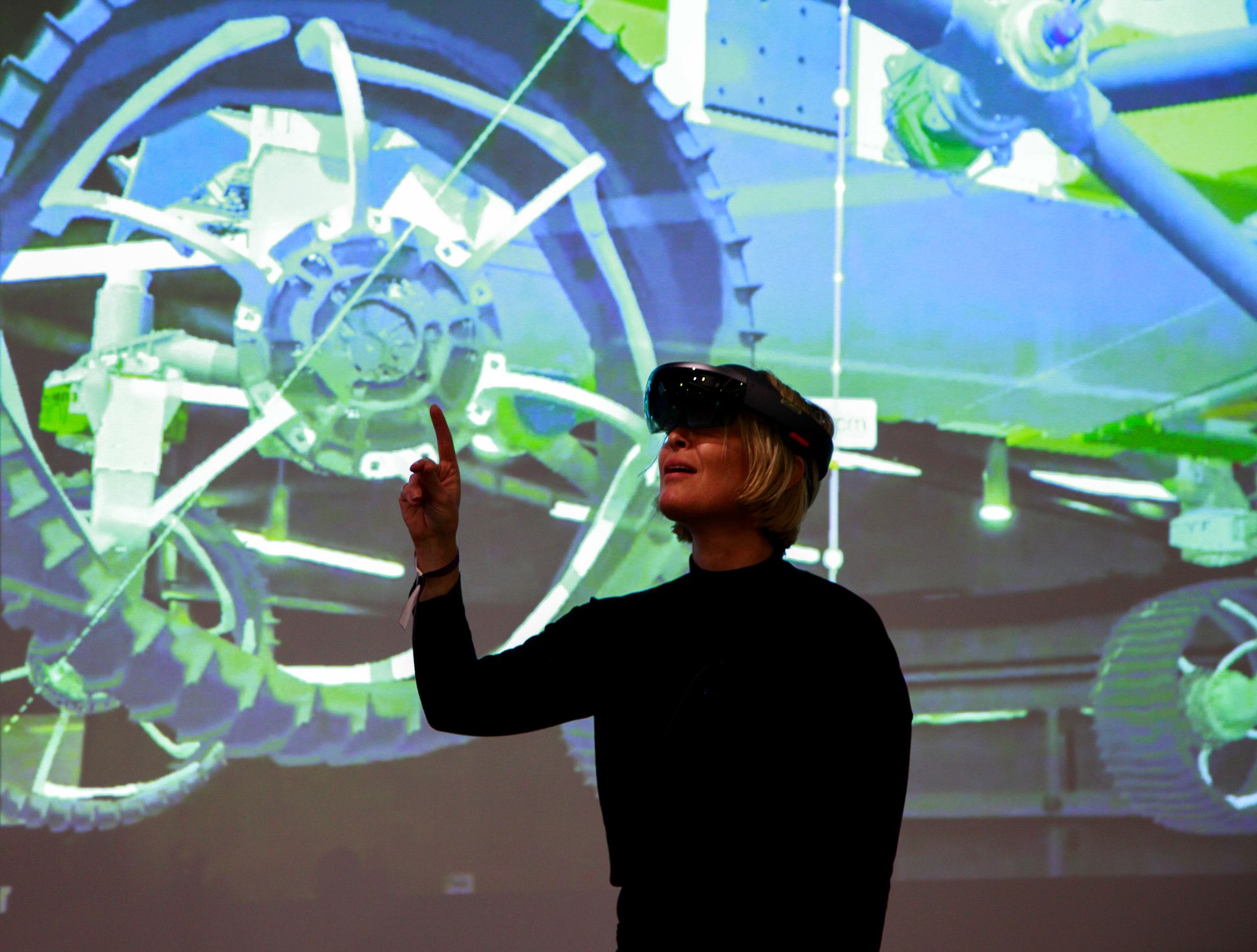
Microsoft, which Computerworld says has been researching quantum computing for more than a decade, is expanding its quantum computing efforts. It has put Todd Holmdahl, one of the people involved in the development of Kinect, HoloLens and Xbox, in charge of developing quantum hardware and software. It’s also hired professors from the Delft University of Technology in the Netherlands; the University of Copenhagen; ETH Zurich and University of Sydney in Australia.