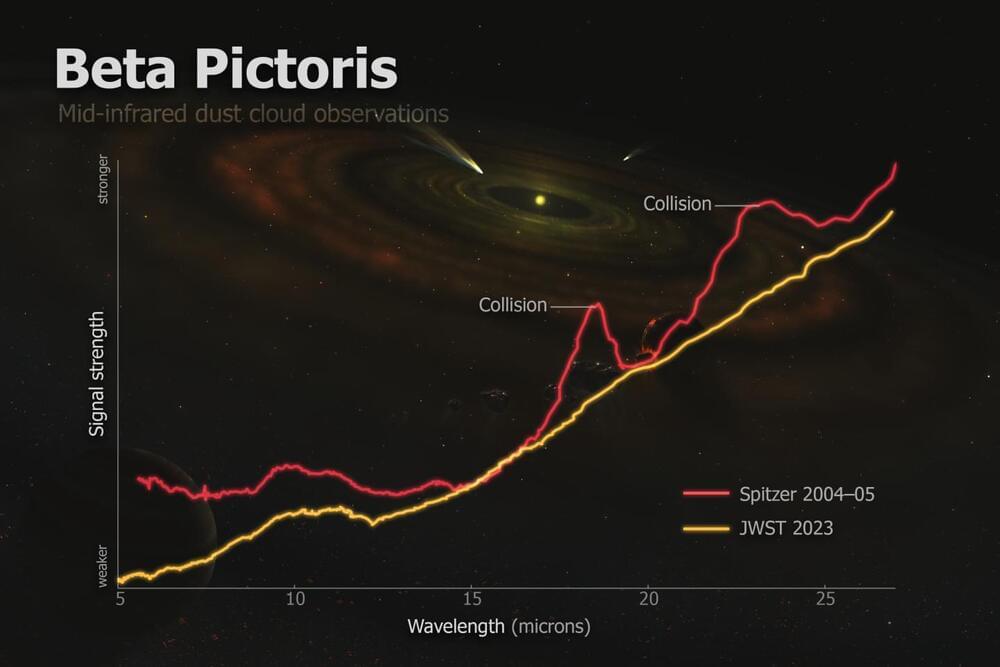
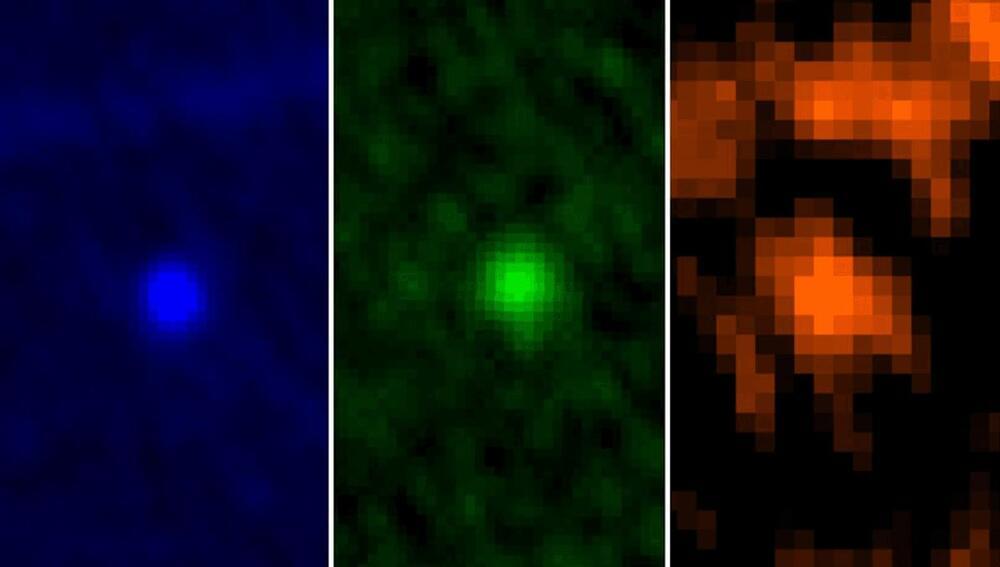
30 years ago, on 16 July 1994, astronomers watched in awe as the first of many pieces of the Shoemaker-Levy 9 comet slammed into Jupiter with incredible force. The event sparked intense interest in the field of planetary defence as people asked: “Could we do anything to prevent this happening to Earth?”
Today, ESA’s Space Safety programme takes another step towards answering this question. The programme has received permission to begin preparatory work for its next planetary defence mission – the Rapid Apophis Mission for Space Safety (Ramses).
Ramses will rendezvous with the asteroid 99,942 Apophis and accompany it through its safe but exceptionally close flyby of Earth in 2029. Researchers will study the asteroid as Earth’s gravity alters its physical characteristics. Their findings will improve our ability to defend our planet from any similar object found to be on a collision course in the future.