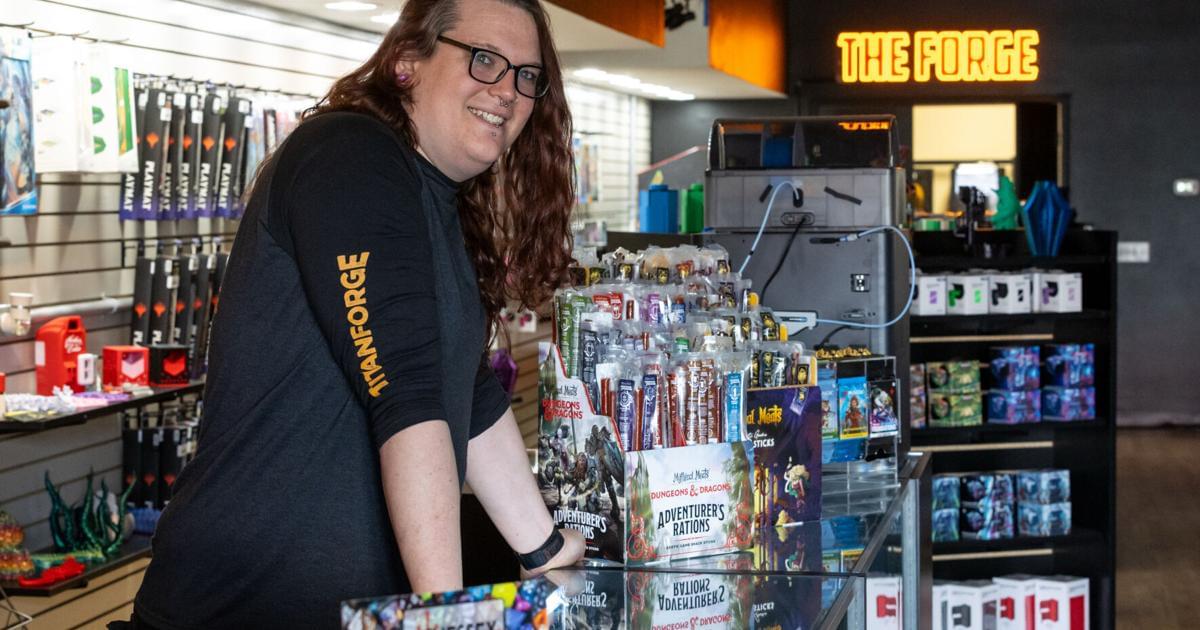
Titanforge 3D Printing & Hobbies will open in downtown Harrisonburg on Friday, bringing cutting-edge technology to the forefront of the city’s cultural district.
For weeks, the massive Elegoo Giga 3D printer in the shop’s front window has elicited excitement from people walking along Main Street near Court Square, with passersby wondering what the huge device could be printing. On Friday, Titanforge will hold its grand opening, giving community members the opportunity see what can be made when materials are piled over three feet high on a 2.6-foot square printing bed.
The shop, spearheaded by Erin Tutwiler, manager of Titanforge, will offer 3D-printed tabletop gaming accessories as well as other retail supplies like trading cards, dice, and game mats. Two kittens, named Titan and Forge, will also be present to greet customers.