Superconductors have intrigued physicists for decades. But these materials, which allow the perfect, lossless flow of electrons, usually only exhibit this quantum-mechanical peculiarity at temperatures so low—a few degrees above absolute zero—as to render them impractical.
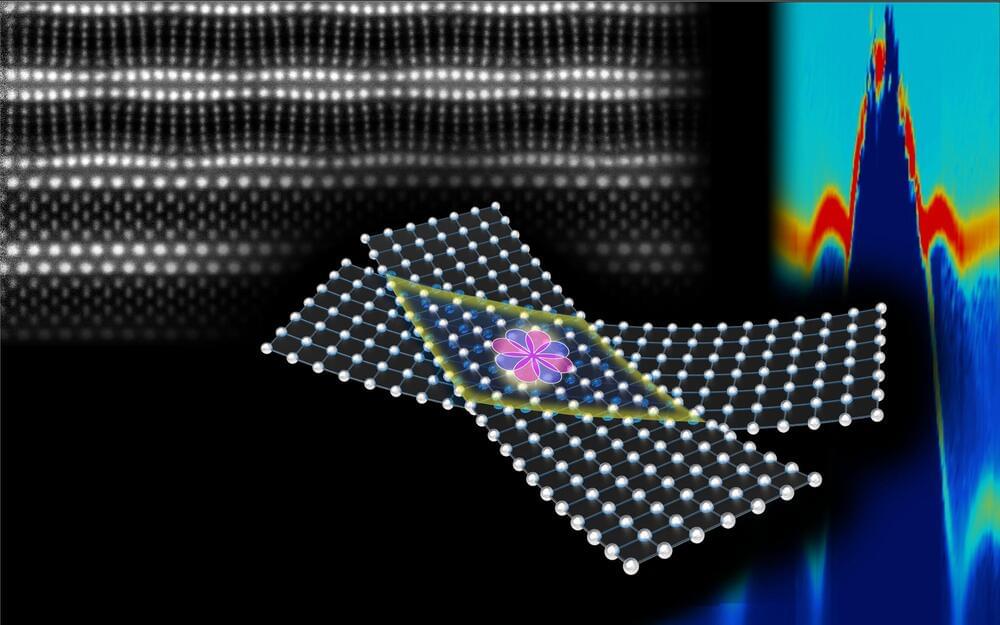
A research team led by Harvard Professor of Physics and Applied Physics Philip Kim has demonstrated a new strategy for making and manipulating a widely studied class of higher-temperature superconductors called cuprates, clearing a path to engineering new, unusual forms of superconductivity in previously unattainable materials.
Using a uniquely low-temperature device fabrication method, Kim and his team report in the journal Science a promising candidate for the world’s first high-temperature, superconducting diode—essentially, a switch that makes current flow in one direction—made out of thin cuprate crystals.