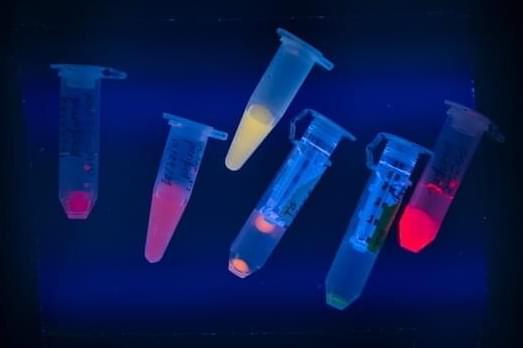
DNA can do more than pass genetic code from one generation to the next. For nearly 20 years, scientists have known of the molecule’s ability to stabilize nanometer-sized clusters of silver atoms. Some of these structures glow visibly in red and green, making them useful in a variety of chemical and biosensing applications.
Stacy Copp, UCI assistant professor of materials science and engineering, wanted to see if the capabilities of these tiny fluorescent markers could be stretched even further—into the near-infrared range of the electromagnetic spectrum—to give bioscience researchers the power to see through living cells and even centimeters of biological tissue, opening doors to enhanced methods of disease detection and treatment.
“There is untapped potential to extend fluorescence by DNA-stabilized silver nanoclusters into the near-infrared region,” she says. “The reason that’s so interesting is because our biological tissues and fluids are much more transparent to near-infrared light than to visible light.”