Synthetic biology offers a way to engineer cells to perform novel functions, such as glowing with fluorescent light when they detect a certain chemical. Usually, this is done by altering cells so they express genes that can be triggered by a certain input.
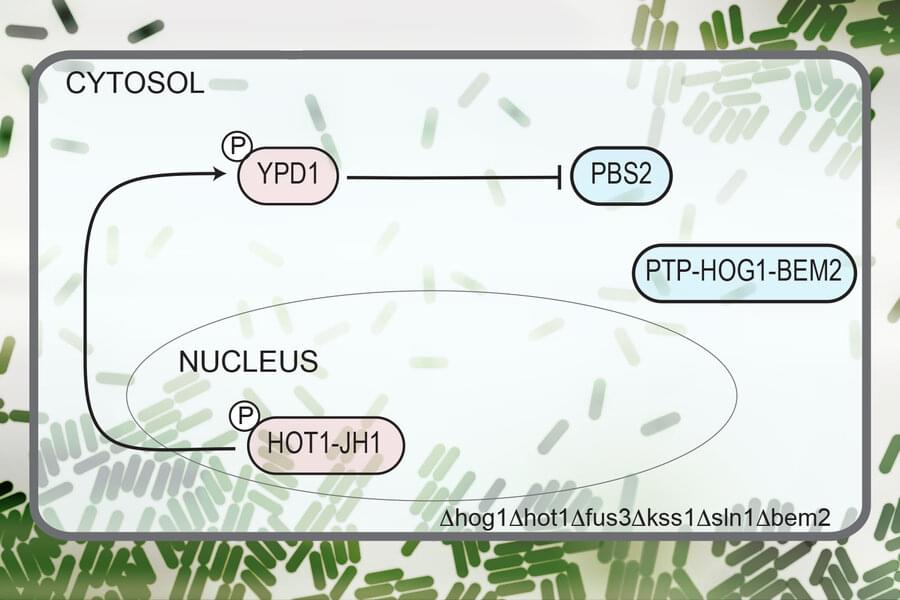
However, there is often a long lag time between an event such as detecting a molecule and the resulting output, because of the time required for cells to transcribe and translate the necessary genes. MIT synthetic biologists have now developed an alternative approach to designing such circuits, which relies exclusively on fast, reversible protein-protein interactions. This means that there’s no waiting for genes to be transcribed or translated into proteins, so circuits can be turned on much faster—within seconds.
“We now have a methodology for designing protein interactions that occur at a very fast timescale, which no one has been able to develop systematically. We’re getting to the point of being able to engineer any function at timescales of a few seconds or less,” says Deepak Mishra, a research associate in MIT’s Department of Biological Engineering and the lead author of the new study.