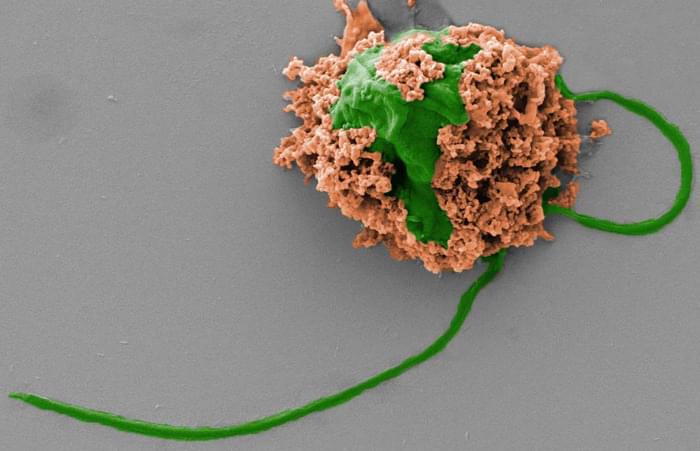
The last decade has brought a lot of attention to the use of microscopic robots (microrobots or nanorobots) for biomedical applications. Now, nanoengineers have developed microrobots that can swim around in the lungs and deliver medication to be used to treat bacterial pneumonia. A new study shows that the microrobots safely eliminated pneumonia-causing bacteria in the lungs of mice and resulted in 100% survival. By contrast, untreated mice all died within three days after infection.
The results are published Nature Materials in the paper, “Nanoparticle-modified microrobots for in vivo antibiotic delivery to treat acute bacterial pneumonia.”
The microrobots are made using click chemistry to attach antibiotic-loaded neutrophil membrane-coated polymeric nanoparticles to natural microalgae. The hybrid microrobots could be used for the active delivery of antibiotics in the lungs in vivo.