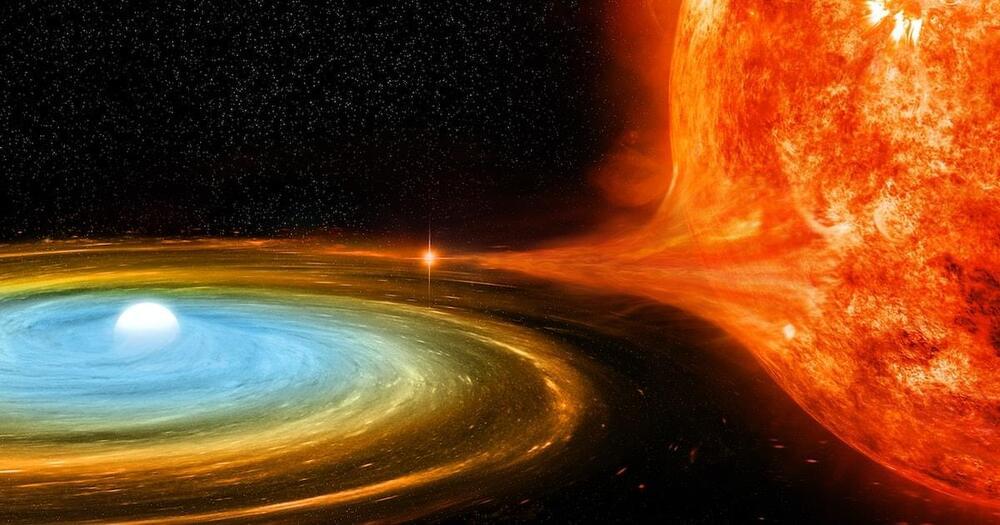
That’s because as a white dwarf draws material away from its hydrogen-burning partner, the stolen gas follows the star’s magnetic field lines in a big, curving arc toward its new home. And in the process, it drains energy from the stars’ whirling dance (so do the gravitational waves produced by their rotation). When that happens, both stars fall toward the shared center of gravity they’re orbiting. Closer orbits also mean shorter orbits, so it takes the stars less time to complete a single lap.
And the closer the stars get, the stronger the gravitational waves they produce, which drains away more energy, so they fall even closer together. By the time they’re close enough to complete an orbit in just a handful of minutes, the donor star has usually run out of hydrogen. That’s why the really close, fast-orbiting cataclysmic binaries tend to be a white dwarf and a helium-burning star.