Scientists at Tokyo Institute of Technology designed a new type of molecular wire doped with organometallic ruthenium to achieve unprecedentedly higher conductance than earlier molecular wires. The origin of high conductance in these wires is fundamentally different from similar molecular devices and suggests a potential strategy for developing highly conducting “doped” molecular wires.
Since their conception, researchers have tried to shrink electronic devices to unprecedented sizes, even to the point of fabricating them from a few molecules. Molecular wires are among the building blocks of such minuscule contraptions, and many researchers have been developing strategies to synthesize highly conductive, stable wires from carefully designed molecules.
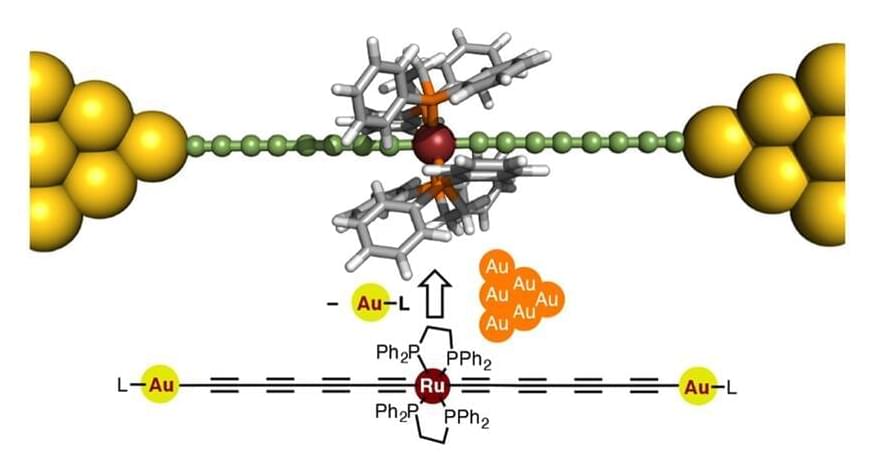
A team of researchers from Tokyo Institute of Technology, including Yuya Tanaka, designed a novel molecular wire in the form of a metal electrode-molecule-metal electrode (MMM) junction including a polyyne, an organic chain-like molecule, “doped” with a ruthenium-based unit Ru(dppe)2. The proposed design, featured in the cover of the Journal of the American Chemical Society, is based on engineering the energy levels of the conducting orbitals of the atoms of the wire, considering the characteristics of gold electrodes.