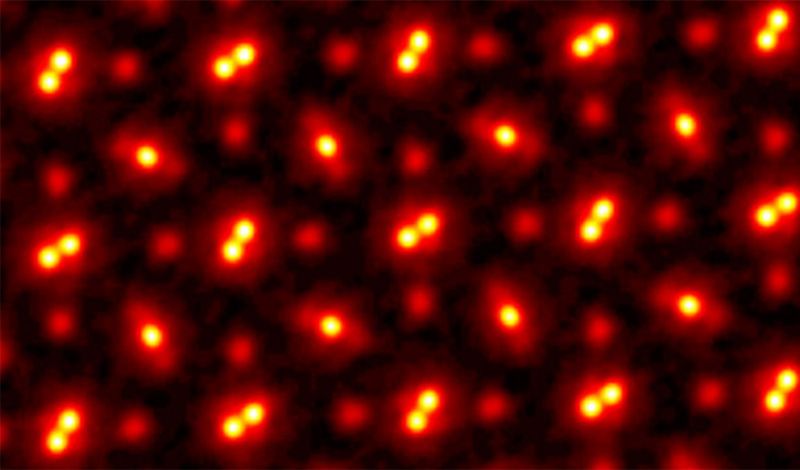
Transmission electron microscopy (TEM) is a technique that involves beaming electrons through a specimen to form an image. This enables the generation of significantly higher resolution than traditional optical microscopes. While the latter devices are typically limited to around 1000x magnification due to the resolving power of visible light, TEM can provide zoom capabilities that are orders of magnitude greater – surpassing even a scanning electron microscope (SEM).
In recent years, TEM instruments have begun to reach extraordinary levels of detail. Spatial resolutions are now edging into the realm of individual atoms, measuring less than 0.0000005 millimetres (mm).
However, TEM is prone to lens aberrations and multiple scattering, limiting its use to samples thin enough to let electrons pass through. The process is technically challenging and requires additional tools to perform. In 2018, researchers at Cornell University offered a potential solution. They built a high-powered detector combined with a new algorithm-driven process called ptychography. This achieved a new record for microscopic resolution, tripling the previous state-of-the-art.