A chance lab discovery is opening up the possibility for wide-scale improvements in drug screening, application of selective painkillers, and selectively nuking cancer cells. The mystery material? Graphene, a semi-metal that’s composed of a single layer of carbon atoms. It’s already being used to make flexible OLED displays and reduce the energy costs of desalination, but its potential benefits for the medical field look promising too.
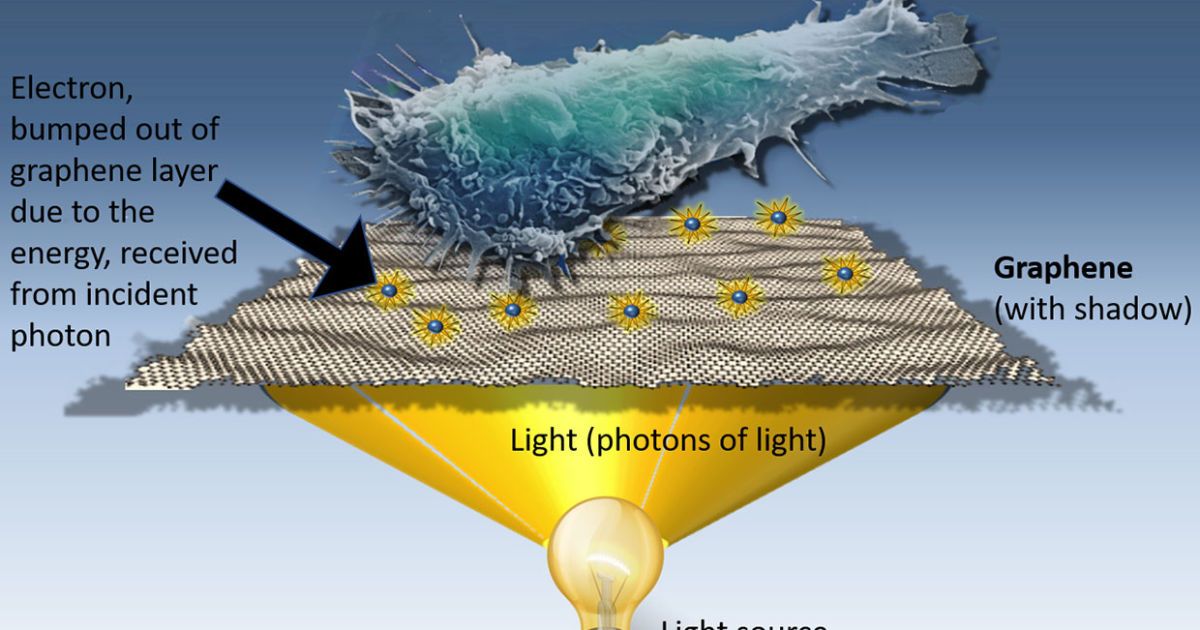
It began with a theory — scientists at the University of California knew graphene could convert light into electricity, and wondered whether that electricity had the capacity to stimulate human cells. Graphene is extremely sensitive to light (1,000 times more than traditional digital cameras and smartphones) and after experimenting with different light intensities, Alex Savchenko and his team discovered that cells could indeed be stimulated via optical graphene stimulation.
“I was looking at the microscope’s computer screen and I’m turning the knob for light intensity and I see the cells start beating faster,” he said. “I showed that to our grad students and they were yelling and jumping and asking if they could turn the knob. We had never seen this possibility of controlling cell contraction.”